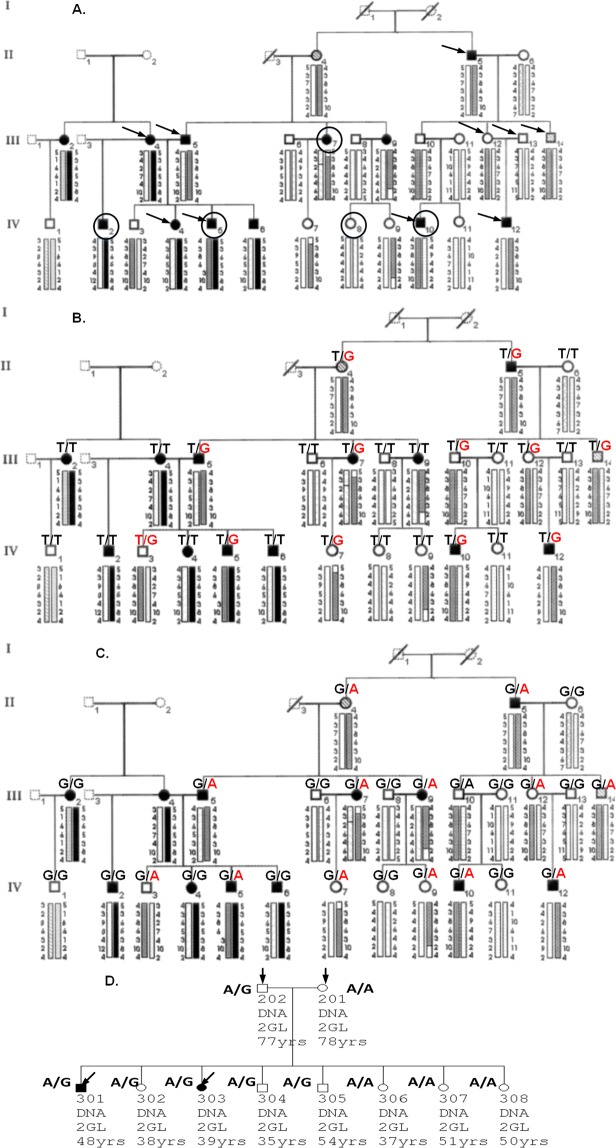
Figure 1.
The pedigree structure and the genotypes of identified pathogenic variants in keratoconus-affected multiplex families with autosomal dominant inheritance using whole exome and whole genome sequencing. (A) The pedigree structure of the four-generation family with keratoconus. Generations are indicated by the Roman numbers I, II, III, and IV on the left side. Individuals in each generation are labeled with Arabic numbers 1 to 14. Linkage haplotypes are labeled under each individual. The gray haplotype is linked with keratoconus. Individuals with dashed lines were not enrolled in the genetic study, while those with the solid lines were consented and enrolled. Subjects with a black arrow were selected for whole exome sequencing while those with a black circle were selected for whole genome sequencing. (B) The alleles are indicated as major allele/minor allele. PPIP5K2 variant rs35471301, p.Ser419Ala, S419A (T/G). Two individuals (III9 and IV9) carrying the linkage haplotype indicated by a grey bar are homozygotes for the major allele T. (C) PCSK1 variant rs373951075 (G/A). All individuals with KC carrying the linkage haplotype indicated by grey bar are heterozygous for the minor allele A. (D) The pedigree structure of a second unrelated multiplex family and the genotypes of a pathogenic variant in the PPIP5K2 gene. Subjects with a black arrow were selected for whole exome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis. Additional individuals were analyzed by PCR-based Sanger sequencing. Allele G is the minor allele.