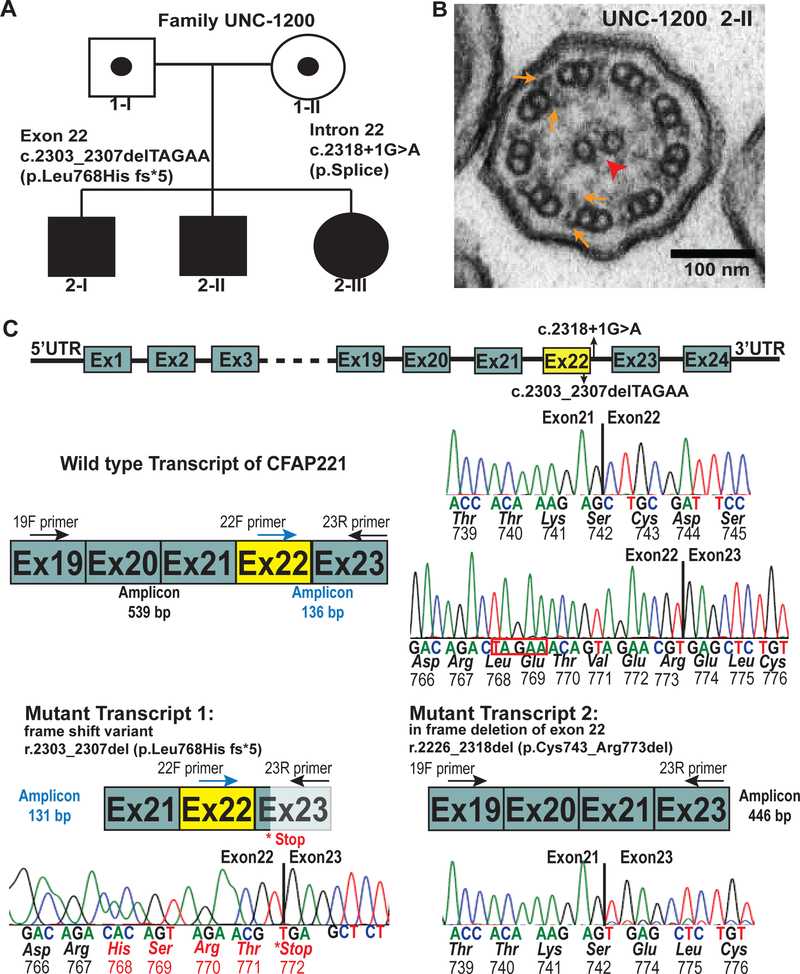
Figure 1: CFAP221 variants in PCD subjects.
(A) Segregation analysis of CFAP221 genetic variants found in family UNC-1200 [c.2303_2307delTAGAA p.Leu768Hiffs*5] and c.2318+1G>A p. splice. Filled symbols indicate PCD affected individuals.
(B) Transmission electron micrograph of axonemal cross sections of nasal epithelium from proband 2-II showing the central pair (arrowhead) surrounded by nine microtubule doublets. Outer dynein arms and inner dynein arms (arrows) project from each doublet normally.
(C) Genomic organization of CFAP221 and sequencing of transcript variants. (top) Schematic representation of the genomic localization of the genetic variants in CFAP221 found in the PCD subjects. Solid box designates exons, horizontal lines designates introns.
(middle) Schematic showing a wild type transcript region of CFAP221 and its corresponding sequencing analysis.
(bottom) Reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction with primers 19F or 22F or 23R (see Supplementary Table 3 for primer sequences) showed two major transcripts. Transcript 1 shows the deletion of 5 bases (highlighted in red box, above), leading to a frame shift of the sequence, resulting in a premature stop codon. Transcript 2 shows the in frame deletion of exon 22. Schematic of wild type and mutant transcripts and the corresponding electropherograms with exact location of the deletions are shown. Primers are designated as F (forward) and R (reverse) in their corresponding cDNA locations. Exon-exon junctions are shown by the vertical solid lines. Base sequence, amino acid sequence, and codon numbers are shown.