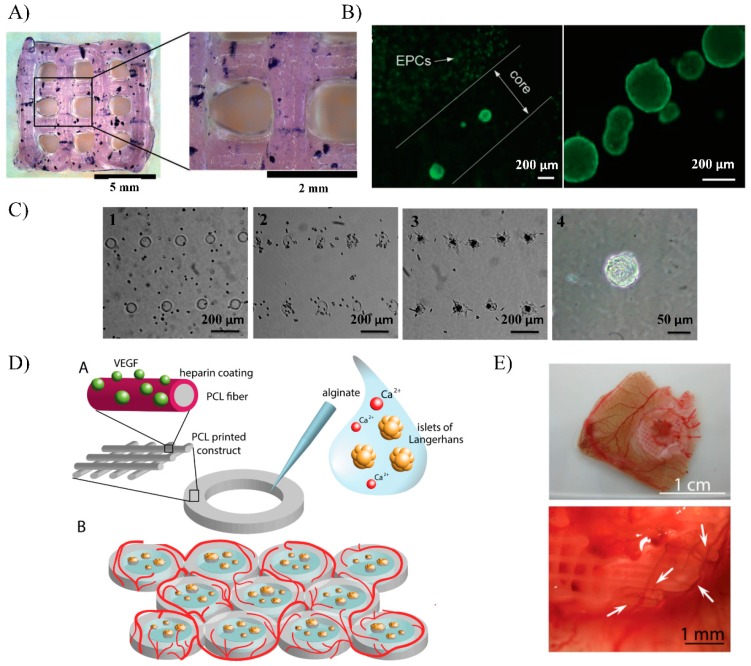
Figure 7.
(A) Bioprinted scaffold by extrusion-based printing with a bioink composed of alginate and methylcellulose where islets are stained for metabolic activity with MTT one day after bioprinting. Scale bars: 5 mm and 2 mm. Adapted from [130] with permission from Duin S. et al., Advanced Healthcare Materials; published by Wiley Online Library, 2019. (B) A coaxial printed construct with encapsulated islets in the core and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in the outer shell. Scale bar: 200 μm. Adapted from [131] with permission from Luis X. et al., Advanced Healthcare Materials; published by Wiley Online Library, 2019. (C) Microscopic images illustrating the formation of pancreatic progenitor cell (PPC) clusters on anisotropic tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) particles conjugated with RGD (arginine−glycine−aspartate) patterned spots at 0 h (1), 3 h (2), 24 h (3), and three days (4) after seeding. The scale bars of 1−3 and 4 are 200 μm and 50 μm, respectively. Adapted from [132] with permission from Yang J et al., ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces; published by ACS publications, 2015. (D) Schematic of the hybrid polycaprolactone (PCL)/alginate scaffold concept. 3D plotted PCL rings were covalently functionalized with a heparin layer. Heparin was used as an active linker to bind VEGF and protect it from degradation. Islets were encapsulated in the inner part of the structure using alginate hydrogel. Multiple constructs can be printed one next to the other in a honeycomb configuration increasing the available surface for islets embedding and revascularization of the scaffold. Adapted from [133] with permission from Marchioli, G. et al., Advanced Healthcare Materials; published by Wiley Online Library, 2016. (E) CAM assay performed with heparin-coated PCL scaffolds loaded with VEGF. Scaffold with 200 ng load VEGF induces blood vessel formation, with normal morphology (Arrows indicate the blood vessel formation). Adapted from [133] with permission from Marchioli, G. et al., Advanced Healthcare Materials; published by Wiley Online Library, 2016.