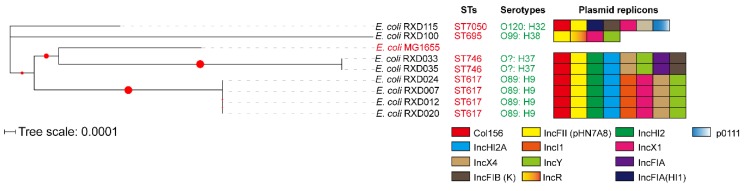
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis of the eight carbapenem-resistant and colistin-resistant E. coli isolates. Sequence types, O-serotypes, H-serotypes, and plasmid replicons are also shown. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the Maximum Likelihood method and Tamura–Nei model. The tree with the highest log likelihood (−13321.25) is shown. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying Neighbor-Join and BioNJ algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the Maximum Composite Likelihood (MCL) approach, and then selecting the topology with superior log likelihood value. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. This analysis involved nine nucleotide sequences. There was a total of 9093 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted by using MEGA X. The circles denote bootstrap values within the range of 0.19–1.000.