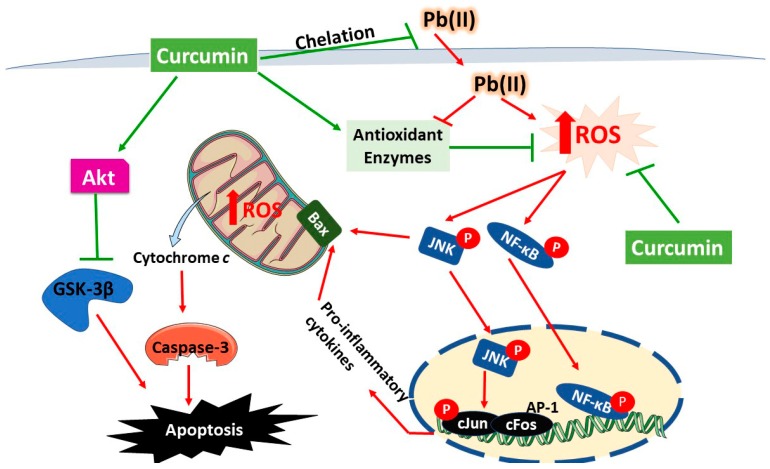
Figure 8.
A schematic diagram illustrating the protective mechanism of curcumin against Pb(II) hepatotoxicity. Pb(II) increases ROS generation and activates NF-κB, JNK and GSK-3β, resulting in inflammation and cell death via apoptosis. Curcumin suppresses ROS production, chelates Pb(II), boosts antioxidant defenses and activates Akt signaling. Akt deactivates GSK-3β through phosphorylation at Ser9.