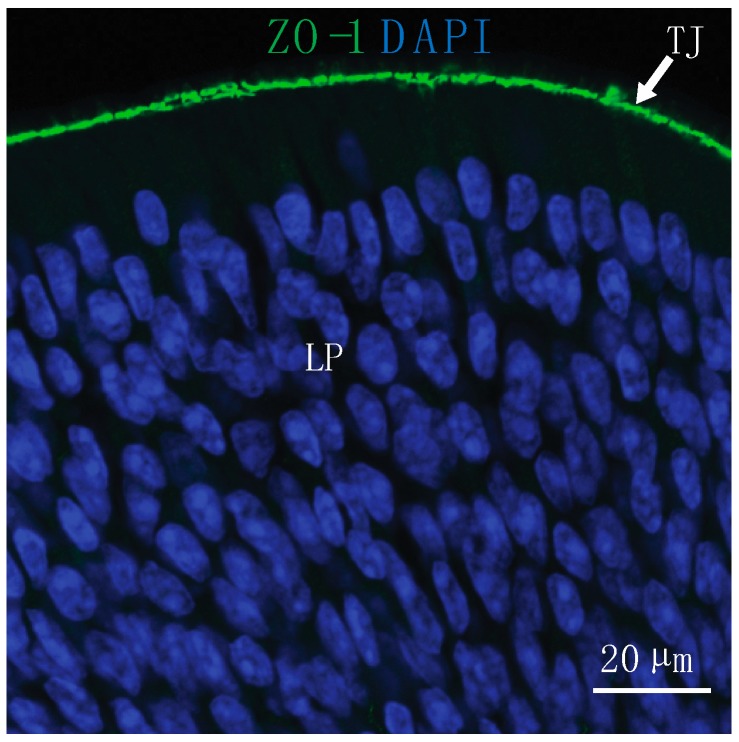
Figure 1.
Substances must reach the lamina propria (LP) of the nasal epithelium through paracellular or transcellular routes to access direct pathways to the brain after intranasal (IN) administration. Tight junctions (TJ) located at the epithelial surface present a barrier for IN drug delivery to the central nervous system (CNS). At the olfactory epithelium, TJ are labeled with an antibody to zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and nuclei are labeled with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI).