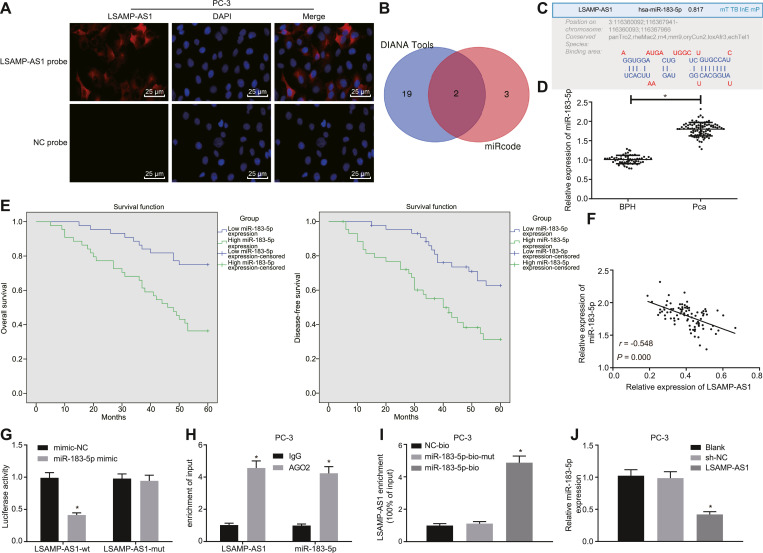
Fig. 4.
LSAMP-AS1 competitively binds to miR-183–5p. A, The subcellular localization of LSAMP-AS1 detected by the FISH assay (200 ×). The green part represents LSAMP-AS1 expression, and blue part represents nucleus. B, miRNAs binding to LSAMP-AS1 screened by DIANA. C, The binding sites of LSAMP-AS1 and miR-183–5p identified by online website RegRNA2.0. D, RT-qPCR to detect the relative expression of miR-183–5p in PCa tissues and BPH tissues. E, Kaplan-Meier analysis on OS and DFS of PCa patients with high and low miR-183–5p expression. F, Pearson correlation analysis of LSAMP-AS1 expression and miR-183–5p expression in PCa tissues. G, The binding of LSAMP-AS1 and miR-183–5p was verified by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. * p < 0.05 versus the mimic-NC group. H, RIP assay to evaluate the binding relationship between LSAMP-AS1 and miR-183–5p. * p <0.05 versus the IgG group. I, RNA-pull down assay of LSAMP-AS1 binding to miR-183–5p. * p <0.05 versus the miR-183–5p-bio-mut group. J, The expression of miR-183–5p in PC-3 cells examined by RT-qPCR. Data in Panel D were analyzed by independent-sample t-test. Data in Panel G, H, I, and J were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. The data were measurement data and presented by mean ± standard deviation. * p < 0.05 versus the BPH tissues or the empty vector group. Cell experiment was repeated 3 times independently.