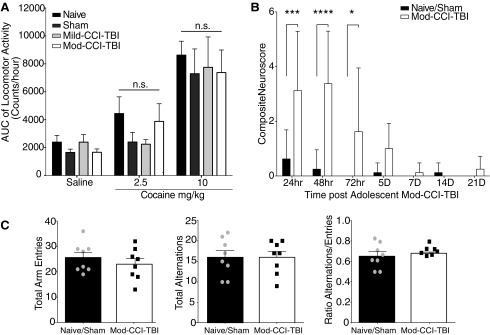
FIG. 2.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) does not alter cocaine-induced locomotor behavior or long-term Neuroscore or Spontaneous Alternation Behavior. (A) Area under the curve (AUC) analysis of locomotor activity. Total locomotor activity recorded as a combination of ambulatory and stereotypy activity counts over 60 min following a single injection of either 0, 2.5, or 10.0 mg/kg cocaine 2 weeks following increasing degrees of adolescent controlled cortical impact model of traumatic brain injury (CCI-TBI). Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). We report an effect of cocaine dose on induced locomotor activity [two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), cocaine dose effect: F (2, 82) = 27.94, p < 0.001], but no effect of brain injury (two-way ANOVA, p > 0.05). (B) Composite Neuroscore includes a battery of neurological motor function tests including forelimb extension, lateral pulsion, forelimb paw placement, hindlimb flexion, and twisting. These were assessed up to 3 weeks following adolescent moderate (Mod)-CCI-TBI, where a maximum total score is 33. Data are presented as mean of errors (total possible score 33 – total actual score) ± SEM. Significant injury effects were observed for the Composite Neuroscore test between naïve and Mod-CCI-TBI mice at 24 [two-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test; Interaction effect of Injury and Time: F (6, 98) = 5.252, p < 0.001], 48 h (DF = 98, p < 0.0001), and 72 h (DF = 98, p < 0.05) post-injury, (Fig. 2B). By 5 days and 1 week post-injury, no difference was observed, indicating Mod-CCI-TBI mice fully recovered from neurological motor deficits prior to the initiation of conditioned place preference (DF = 98, p > 0.05). (C) Spontaneous alternations were measured using the Y-Maze test at 2 weeks following adolescent Mod-CCI-TBI. Total number of arm entries and alternations were recorded for a total of 5 min. We report no differences in total number of arm entries, total number of alternations, or ratio of alternations/entries in adolescent naïve vs. Mod-CCI-TBI mice (unpaired t-tests, two-tailed, t = 0.0, DF = 14, p > 0.05). n = 8 mice per condition.