Figure 1.
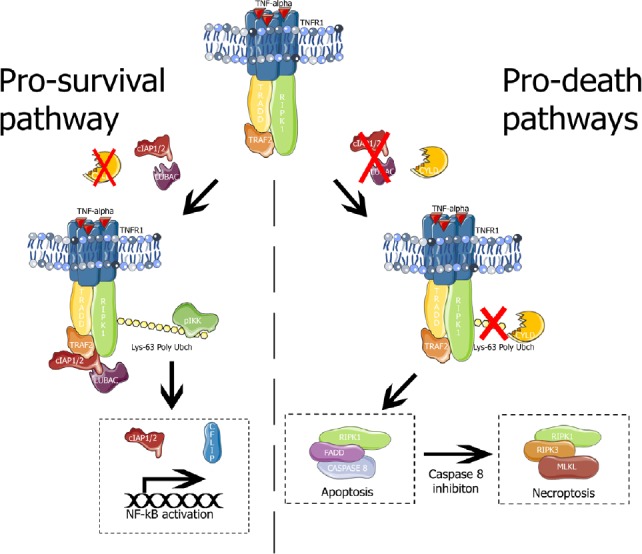
TNFR1 signaling.
Left panel, pro-survival pathway elicited by TNFR1 complex I (TNFR1, TRADD, RIPK1, TRAF2, cIAP1/2 and LUBAC). The E3 ubiquitin ligases cIAP1/2 and LUBAC cause Lys63 polyubiquitination of RIPK1. Polyubiquitinated-RIPK1 serves as scaffold for recruitment and activation of IKK which activates NF-κB promoting the transcription of pro-survival genes (such as cIAP1/2 and cFLIP). Right panel, pro-death pathways. In absence of E3 ubiquitin ligases, or in the presence of the deubiquitinase CYLD, RIPK1 forms the complex II (RIPK1, FADD and caspase 8) which leads to extrinsic apoptosis. If caspase 8 is inhibited, complex II is dissembled and RIPK1 forms necrosome complex (RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL) that phosphorylates MLKL, the necroptosis executioner. cFLIP: Cellular FLICE (FADD-like IL-1β-converting enzyme)-inhibitory protein; cIAP1/2: cellular inhibitors of apoptosis 1/2; CYLD: ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase; FADD: Fas-associated death domain; IKK: IκB kinase; LUBAC: linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex; MLKL: mixed lineage domain-like protein; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; RIPK1: receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1; TNFR1: tumor necrosis factor receptor 1; TRADD: receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein; TRAF2: TNFR-associated factor 2.
