Figure 4.
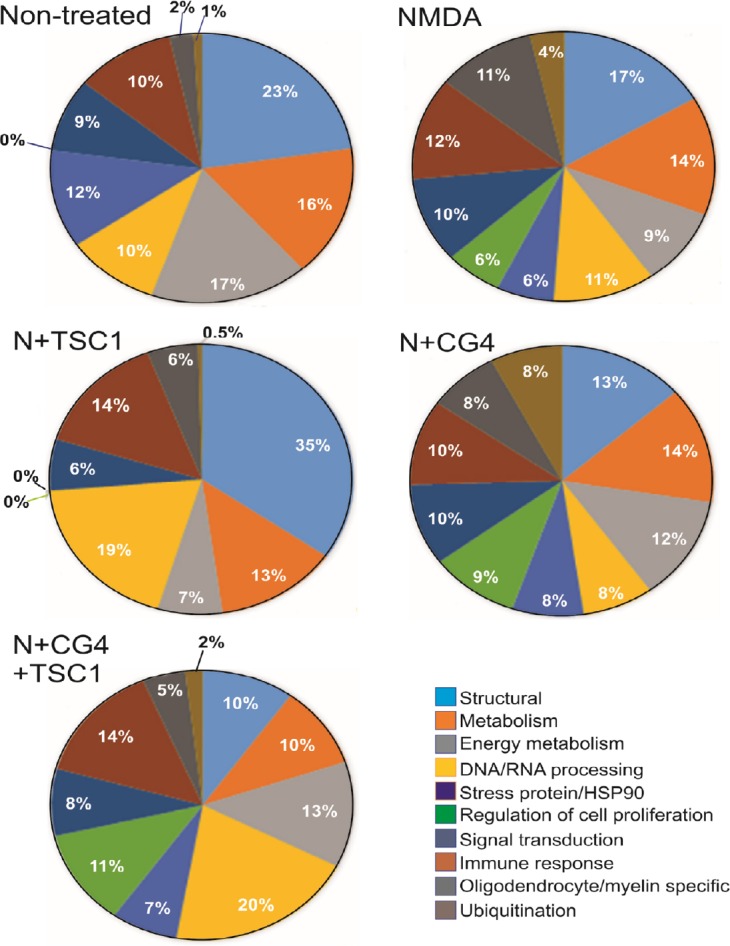
Comparison of the proteomic profile using the functional enrichment score and taking into account significant hits only.
We found that the percentage of the proteins varied considerably across treatments in the brains of non-treated mice and those exposed to the specific treatments: NMDA (N), N + TSC1, N + CG4-OLPs, N + TSC1 + CG4-OLPs, in particular structural proteins, reduction of DNA/RNA and proliferation-related proteins. There was no significant expression of HSP90 in mice treated with N + TSC1 and a reduced percentage was found in mice receiving CG4-OLPs in the presence of NMDA whereas 12% was expressed in non-treated mice, these results include both HSP90 alpha and beta. Ubiquitination fluctuated between virtually 0 and 8% where in animals receiving TSC1 with or without grafted CG4-OLPs the ubiquitination percentage ranged between 0 and 2%. In contrast, mice injected with just NMDA showed 4% ubiquitination and mice injected with NMDA + CG4-OLP grafts reached 8% indicating that CG4-OLPs, derived from rat brain, are more vulnerable to NMDA than mouse OLPs. CG4: Central glial 4 cells; HSP90: heat shock protein 90; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate; OLPs: oligodendrocyte progenitors; TSC1: the combination of transferrin and insulin growth factor 1.
