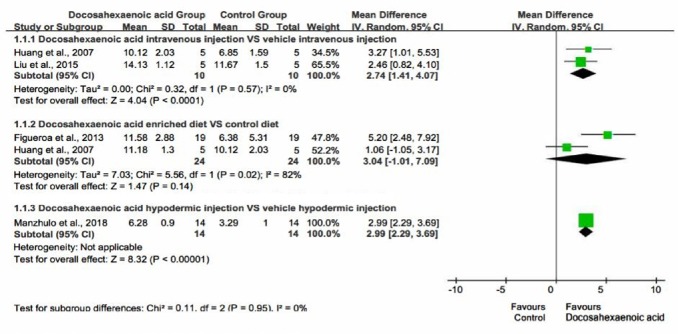
Figure 5.
Effect of oral, intravenous, and hypodermic injection of docosahexaenoic acid on Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan scale scores.
Intravenous and hypodermic injection of docosahexaenoic acid significantly promoted the recovery of motor function in spinal cord injury rats. However, the recovery of motor function was not as marked in rats that received oral administration of docosahexaenoic acid compared with intravenous injection docosahexaenoic acid.