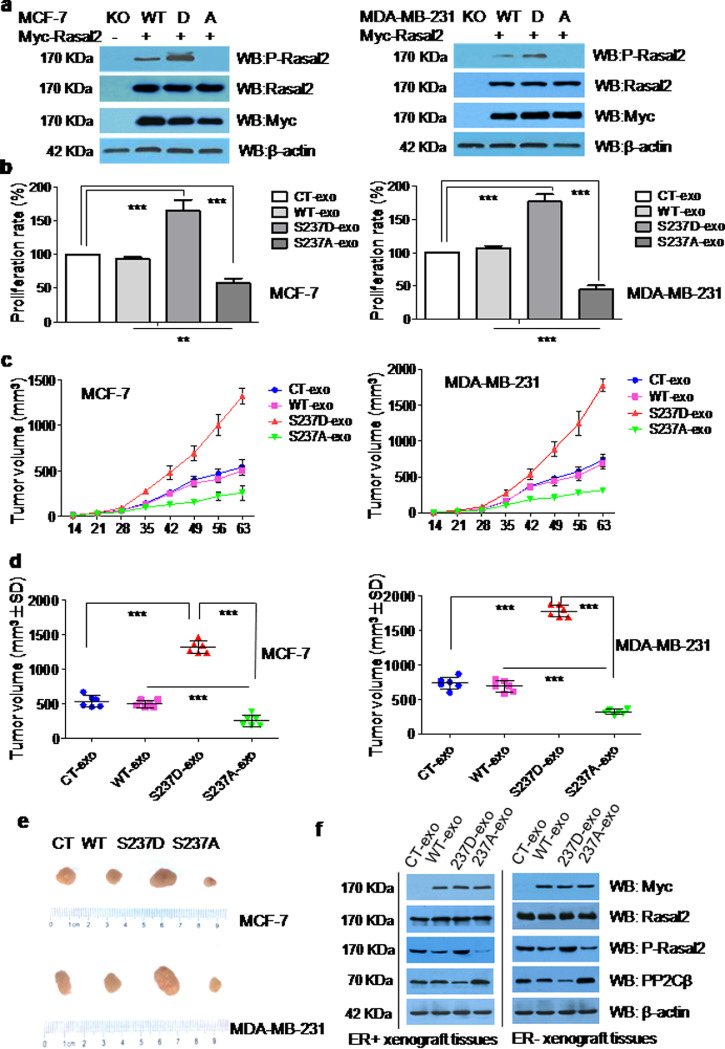
Fig. 5.
The phosphorylation of Rasal2 at S237 in PH domain facilitates tumourprogression via exosomal secretion. (a) Construction of A and D mutant of Rasal2 at S237. Myc-Rasal2 (WT, S237D, S237A) plasmids were transfected into Rasal2 KO cells and transfection efficiency was analysed with anti-Rasal2 and anti-myc antibodies by immunoblot analysis in the lysates of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells; (b) proliferation rate. 0.05 μg/μl of autologous CT-exo, WT-exo, S237D-exo and S237A-exo were respectively co-incubated with tumour cells for 24-h, the proliferation rate was then evaluated by CCK-8 assay. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = =3). ***p < 0.001 vs. CT-exo or WT-exo (t-test, two-tailed); (c) tumour volumes. MCF-7 cells and MDA-MB-231 cells were injected into nude mice (6 mice/group). After two weeks’ inoculation, 5 μg of autologous CT-exo, WT-exo, S237D-exo and S237A-exo were respectively injected into mice in tail vein for two times a week continued for seven weeks and the growth rate of tumours were measured and tumour volumes (mm³) calculated on each of the indicated days after inoculation, each point representing the mean calculated volume of six tumours; (d) tumour volumes were measured after nine weeks inoculation. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = =6). **p < 0.01,***p < 0.001; vs. CT-exo, WT-exo or S237D-exo(t-test, two-tailed); (e) the size of tumours; (f) the expression of Rasal2, P-Rasal2 (S237) and PP2Cβ by immunoblot analysis in the lysates of mice xenograft tumour tissues.