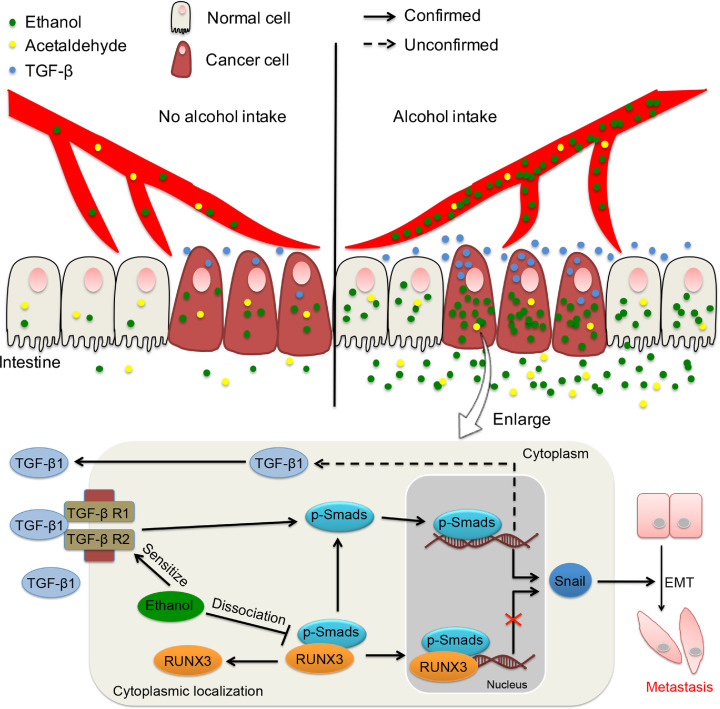
Fig. 9.
Graphical abstract of this study. The colorectum of most patients with alcohol-related CRC is exposed to a high circulating level of ethanol after drinking, and CRC cells exhibit an extremely impaired ethanol metabolism. Ethanol itself enhances the migration/invasion of CRC by promoting EMT via the TGF-β/RUNX3/Snail axis. PFD might be a novel therapeutic strategy for the management of CRC by targeting TGF-β signalling.