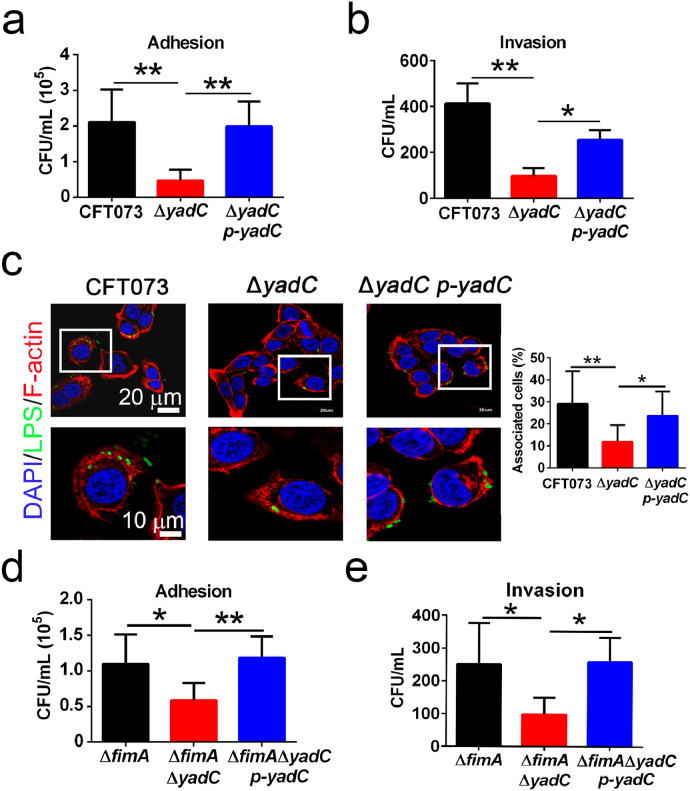
Fig. 1.
YadC is involved in UPEC adhesion and invasion to bladder epithelial cells.
Adhesion (a) and invasion (b) assays of CFT073, ΔyadC or ΔyadC p-yadC. 5637 cells were infected with bacteria at an MOI of 15 (n = 3). (c) Immunofluorescence analysis of 5637 cells infected with CFT073, ΔyadC or ΔyadC p-yadC at an MOI of 5 for 2 h (n = 3, three combined independent experiments each with four different fields). Blue, nucleus; Green, LPS; Red, F-actin. The percentage of associated cells was calculated by total bacteria-associated cells dividing total cells in all fields. Scale bar, 20 μm. Adhesion (d) and invasion (e) assays of ΔfimA, ΔfimAΔyadC, or ΔfimAΔyadC p-yadC. 5637 cells were infected with bacteria at an MOI of 50 (n = 3, three independent experiments). Data are the mean ± SD, one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.