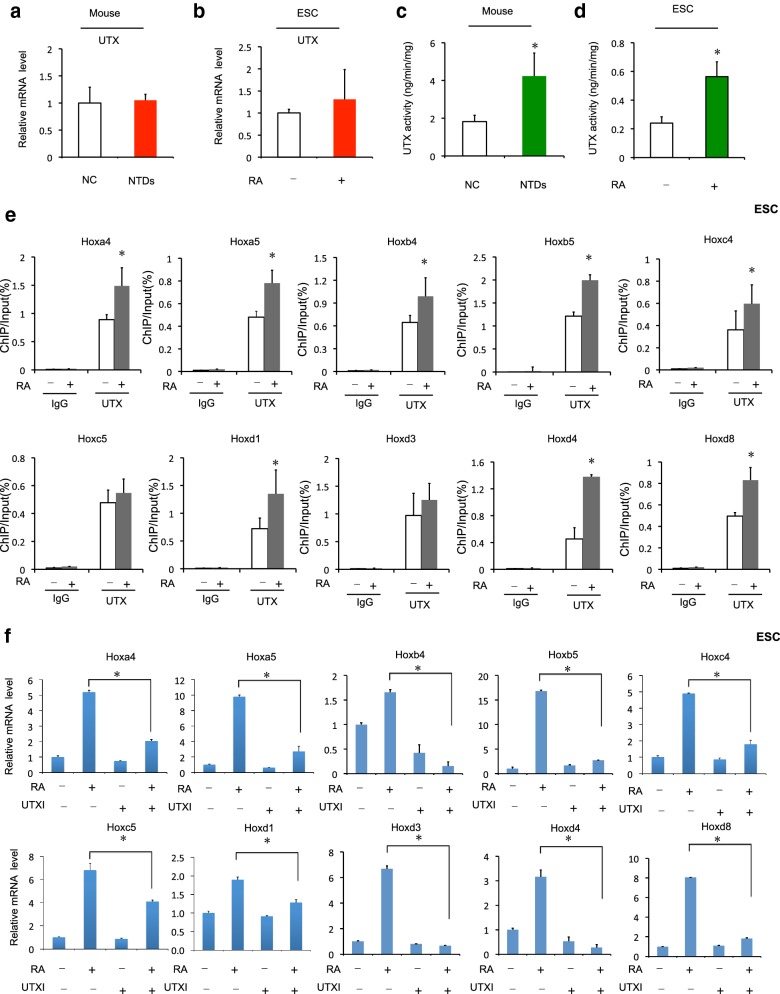
Fig. 5.
UTX activity plays the important role in RA-induced Hox upregulation. a UTX mRNA in cranial neural tissue of RA-induced mouse NTDs was measured by RT-qPCR. Actb was used as a loading control. Data are shown as the mean (SD; n = 4). *P < 0.05. b UTX mRNA in mouse ESCs treated with RA was measured by RT-qPCR. Actb was used as a loading control. Data are shown as the mean (SD; n = 3). *P < 0.05. c UTX demethylase activity was detected in cranial neural tissue of RA-induced NTD mouse embryos. Data are shown as the mean (SD; n = 4). *P < 0.05. d UTX demethylase activity was detected in mouse ESCs after RA treatment. Data are shown as the mean (SD; n = 3). *P < 0.05. e ChIP assays of UTX were performed using mouse ESCs treated with 1 μM RA for 24 h. Mouse IgG was used as control. Enrichment of Hox gene promoters was measured by qPCR. f GSK-J4 (UTX inhibitor) affected mRNA levels of Hox genes in RA-induced mouse ESCs. Mouse ESCs were treated with GSK-J4 (30 nM) for 6 h. Then, after 24 h of RA treatment, cells were collected and analyzed. Data are shown as the mean (SD; n = 3)