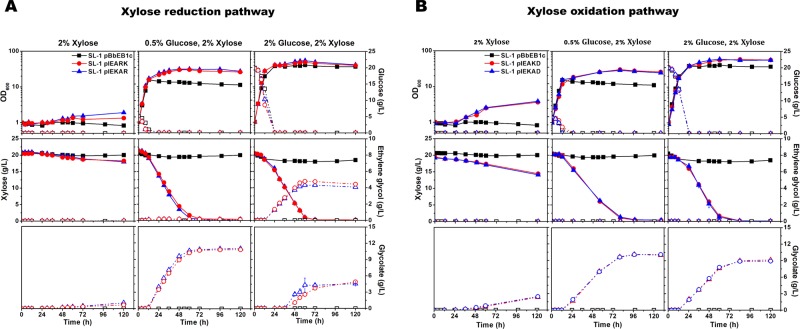
Figure 2.
Time course of growth, xylose consumption, and ethylene glycol and glycolate production in engineered C. glutamicum. Growth and carbon source consumption in recombinant C. glutamicum for the production of ethylene glycol (A) and glycolate (B). Optical densities at 600 nm (OD600; solid symbol; solid line) and glucose (open symbol; dashed line) concentrations [upper row], xylose (solid symbol; solid line) and ethylene glycol (open symbol; dashed line) concentrations [middle row], and glycolate (open symbol; dashed line) concentrations [lower row] in the medium were measured for C. glutamicum SL-1 pBbEB1c (black square in A and B), SL-1 pIEARK (red circle in A), SL-1 pIEKAR (blue triangle in A), SL-1 pIEAKD (red circle in B), and SL-1 pIEKAD (blue triangle in B). Either xylose (2% wt/vol) as the sole carbon source [left panel], a mixture of xylose (2% wt/vol) and glucose (0.5% wt/vol) [middle panel], or a mixture of xylose (2% wt/vol) and glucose (2% wt/vol) [right panel] in CgXII medium was used. The data represent mean values of triplicate cultivations, and the error bars represent standard deviations. See Table 1 for the strains used.