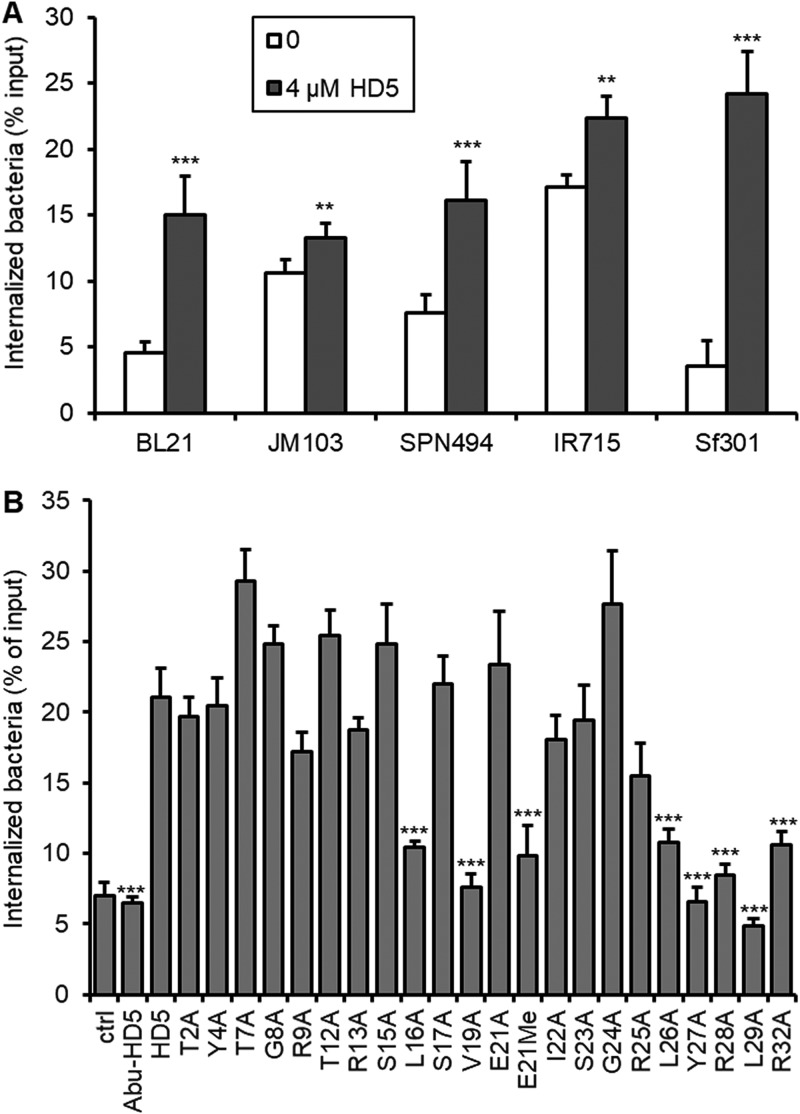
FIG 2.
(A) HD5 promotes internalization of E. coli and Salmonella strains into macrophages. Internalization assays were performed on nonfimbriated E. coli strain BL21, fimbriated E. coli strain JM103, wild-type Salmonella Typhimurium strain IR715, and its flagellum/fimbria-dual mutant strain SNP494; Sf301 was included for comparison. Data are shown as means ± SDs from at least three independent experiments. Statistical significance was calculated (for HD5-treated groups compared to vehicle controls [0]) using a Student's t test. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (B) Structural determinants of HD5 for its activity of promoting bacterial internalization into macrophages. Linear HD5 analog Abu-HD5, dimerization-debilitating analog E21Me, and a panel of alanine-substitution mutants were analyzed in the Shigella internalization assay. Wild-type HD5 and mock-treated control were included for comparison. Data are shown as means ± SDs from at least three independent experiments. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) in comparison with wild-type HD5. ***, P < 0.001.