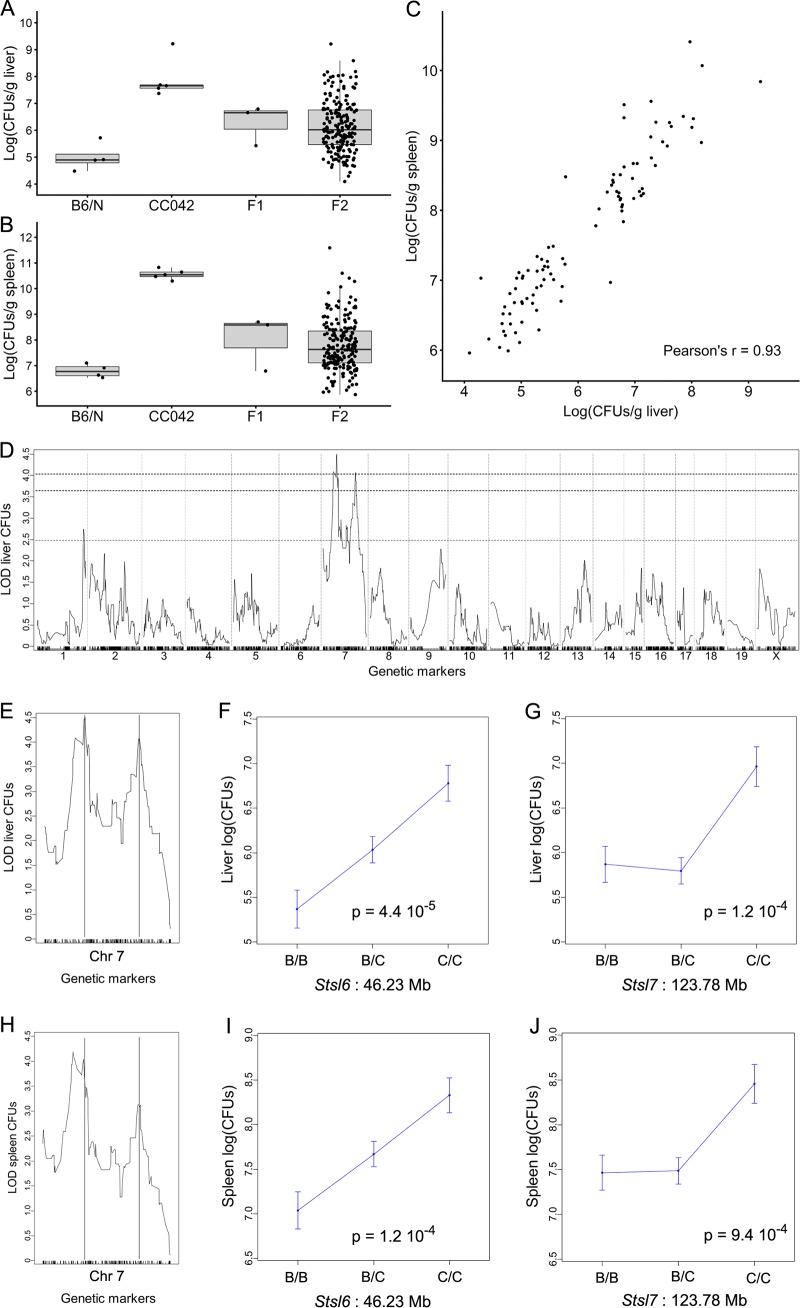
FIG 6.
Susceptibility of CC042 mice to S. Typhimurium is controlled by two linked loci on chromosome 7. (A and B) Bacterial load in liver (A) and in spleen (B) at day 4 postinfection with S. Typhimurium in C57BL/6NCrl (n = 4), CC042 (n = 5), (C57BL/6NCrl × CC042)F1 (n = 3), and (C57BL/6NCrl × CC042)F2 (n = 196) mice. Bacterial loads in F2 mice spanned the values for the two parental strains. (C) Bacterial loads in the 94 individuals selected for genotyping, showing a strong correlation between the two organs (Pearson’s r = 0.93). (D) Genome-wide QTL mapping of the liver bacterial load identified two statistically significant peaks on chromosome 7. The horizontal dashed lines indicate the 0.05, 0.1, and 0.63 (top to bottom) significance thresholds estimated from 10,000 permutations. (E, H) QTL positions are indicated by vertical lines in liver (E) and in spleen (H). See Table 3 for details on each QTL. (F, G, I, J) The proximal Stsl6 QTL acted semidominantly on liver (F) and on spleen (I) bacterial loads, while the CC042-inherited allele at the distal Stsl7 QTL had a recessive mode of action both for liver (G) and for spleen (J). For both QTLs, the CC042-inherited allele was associated with an increased bacterial load. B, the B6 allele; C, the CC042 allele.