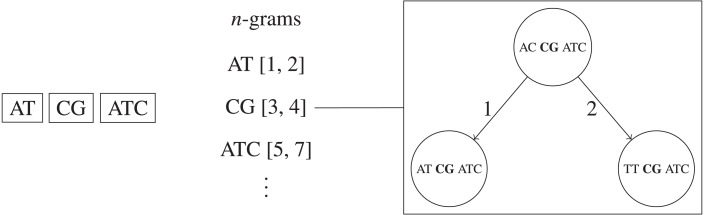
Figure 4. Simplified example of the n-grams BK-trees data structure.
If two edits are allowed, then each UMI is split into three non-overlapping n-grams. Each n-gram sequence and its interval position in the full UMI sequence corresponds to a BK-tree that contains all UMIs that the same n-gram sequence at the same position.