Fig. 1.
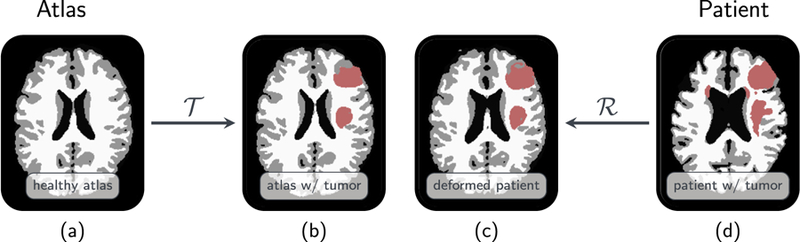
Here we summarize the joint registration and biophysical inversion in SIBIA. (a) shows the segmented healthy brain (the atlas), (b) tumor-bearing atlas brain generated by biophysical simulation, (c) patient tumor registered to atlas (in atlas space), (d) tumor-bearing patient brain. The inputs are the images (a) and (d). The outputs are the tumor growth parameters, the registration parameters, and images (b) and (c). Here is the forward tumor map, which given image (a) grows a tumor and generates image (b). Similarly, is the forward registration map, which given image (d) generates image (c). In SIBIA, we compute tumor-growth parameters and registration parameters so that images (b) and (c) are as similar as possible (in the L2 norm). In this example, the biophysical tumor growth parameters are the initial conditions for a reaction–diffusion equation. The registration is parameterized using an Eulerian framework and a velocity field that is used to advect image (d) to image (c).
