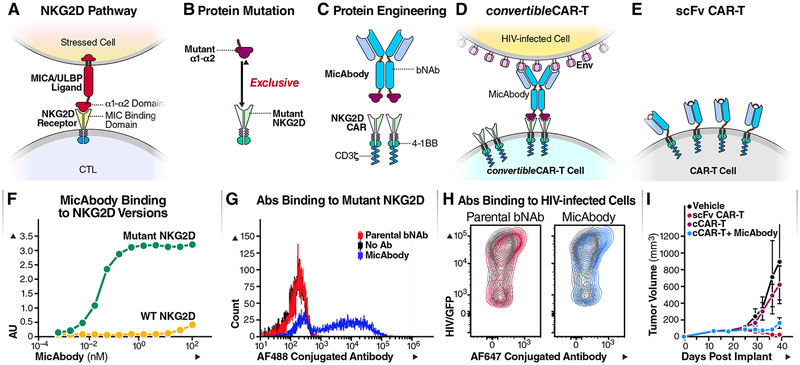
Figure 1: Construction of MicAbody/ConvertibleCAR-T Platform.
(A) The MIC/ULBP-ligand family are natural ligands for NKG2D receptors present on NK cells and CTLs. NKG2D binds to the α1–α2 part of the ligands (B) Protein engineering of the α1–α2 ligand domain and NKG2D receptor to create a cognate ligand-receptor pair that no longer recognizes the natural ligand or receptor. (C) Protein engineering of bispecific antibody based on bNAb and mutated α1–α2 on the antibody (MicAbody), and a mutated NKG2D CAR fused to 4–1BB and CD3ζ as the signaling domains. (D) Construction of cCAR-T cell based on the mutated NKG2D. The convertibleCAR system allows specific binding of MicAbody to the mutated NKG2D-based CAR expressed on the T-cell. (E) Conventional scFv-based CAR-T cell. (F) ELISA binding assay of MicAbody to WT NKG2D receptor or to the mutated form. AU – arbitrary absorbance units. The figure represents one of three independent biological experiments yielding similar results. (G) Antibodies conjugated to Alexa flour (AF) fluorophore were assessed for selective binding of to cCAR-T cell with mutated NKG2D. Blue- MicAbody; Red- parental bNAb; Black-no Ab. 10,000 events were acquired and each dot represents number of cells with the same MFI. (H) MicAbody binds to HIV/GFP+ cells similarly to the parental bNAb. Red- parental bNAb; Blue- MicAbody; Gray- Isotype control. See also Tables S1 and S2. (I) In vivo killing by the cCAR-T platform. Comparison of the effectiveness of cCAR-T platform with the scFv conventional CAR-T platform in controlling Raji lymphoma cell growth in NSG mice. n=3 for each cohort.