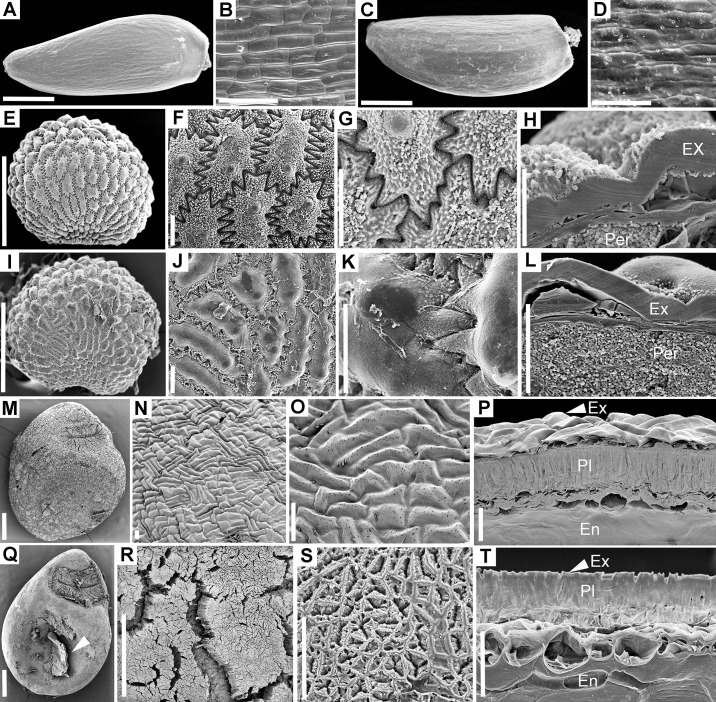
Fig 4. Scanning electron microscopy of seed coat or pericarp in control and passed diaspores.
A–D. Cirsium brachycephalum. A–B. Control cypselae. A. General morphology. B. Surface of exocarp. C–D. Passed cypselae. A. General morphology. D. Surface of exocarp showing minor chips/abrasions of excocarp cuticle. E–L. Lychnis coronaria. E–H. Control seeds. E. General morphology. F. Surface of exotesta. G. Detail of exotesta surface. H. Cross-section through the seed coat. I–L. Passed seeds. I. General morphology. J. Surface of exotesta. K. Surface of exotesta detail. L. Cross-section through the seed coat; in all images of passed seeds note that epicuticular wax was stripped from the convex areas of exotesta cells. M–T. Cuscuta lupuliformis. M–P. Control seeds. M. General morphology. N–O. Seed surface (exotesta). P. Cross-section through seed coat and endosperm. Q–T. Passed seeds. Q. General morphology; arrow indicates remnants of exotesta after passing. R. Cracks opened within the palisade layer reaching to the endosperm. S. Surface of palisade layer after the removal of exotesta. T. Cross- section through seed coat and endosperm showing the palisade layer left as the most exterior seed layer. Ex = exotesta; Hil = Hilum area; Per = perisperm; Pl = palisade layer. Scale bars. A, C, E, I, M, Q, R = 0.5 mm; B, D, H, L = 30 μm; F, G, J, K, N, O, P, S, T = 50 μm.