FIG. 2.
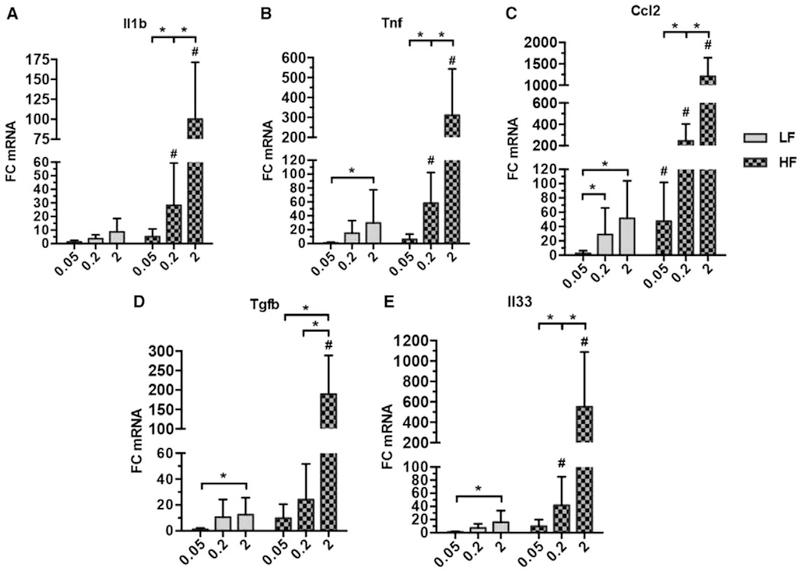
Dietary cholesterol increases hepatic expression of proinflammatory and profibrotic cytokines in a dose-dependent manner. (A-E) Whole-liver expression of inflammation and fibrosis mediators in mice fed for 12 weeks as measured by real-time quantitative PCR. Bars represent the average FC normalized to the average of LF.05 ± standard deviation of each dietary group (4–7 mice per group). Rn18s was used as a reference gene for each analysis. Statistical significance was determined using the Mann-Whitney U test. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.05 compared to corresponding low-fat diet.
