Figure 3.
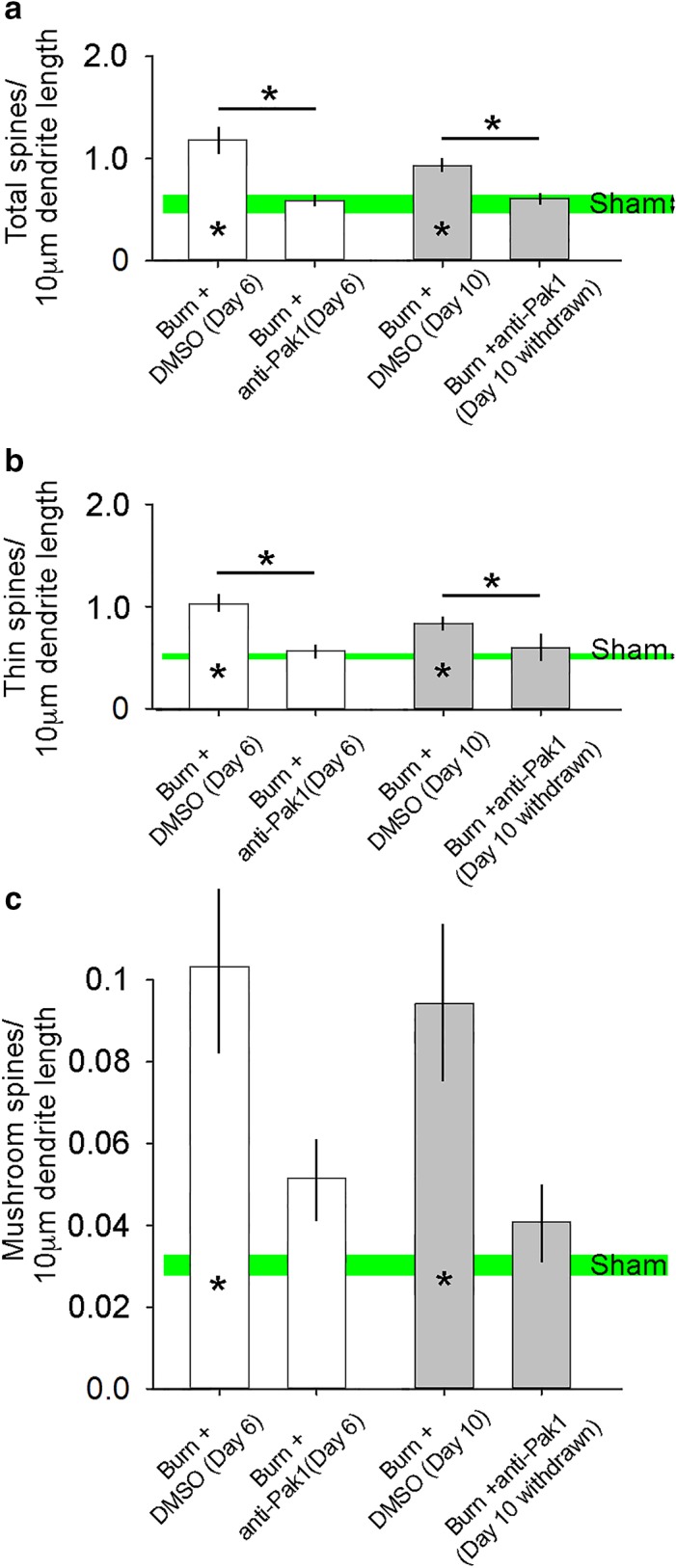
Dendritic spine density on alpha‐motor neurons. 6 days after burn injury, (a) total, (b) thin, and (c) mushroom dendritic spine density increased on ipsilateral motor neurons following second‐degree burn injury treated with control DMSO, as compared with Sham (* within bar = p < .05). At 10‐days postburn injury with DMSO treatment, dendritic spine density for all types also remained elevated as compared with Sham (* within bar = p < .05). Although treatment with anti‐Pak1, romidepsin, reduced total and thin‐shaped dendritic spine density at Day 6 and following the drug's withdrawal by Day 10 following burn injury, romidepsin had no significant effect on mushroom‐shaped dendritic spines following burn injury on alpha‐motor neurons. In general, there was no difference in dendritic spines in burn‐injured animals treated with anti‐Pak1‐inhibitor and Sham animals (n.s.). Data are shown as mean ± SEM
