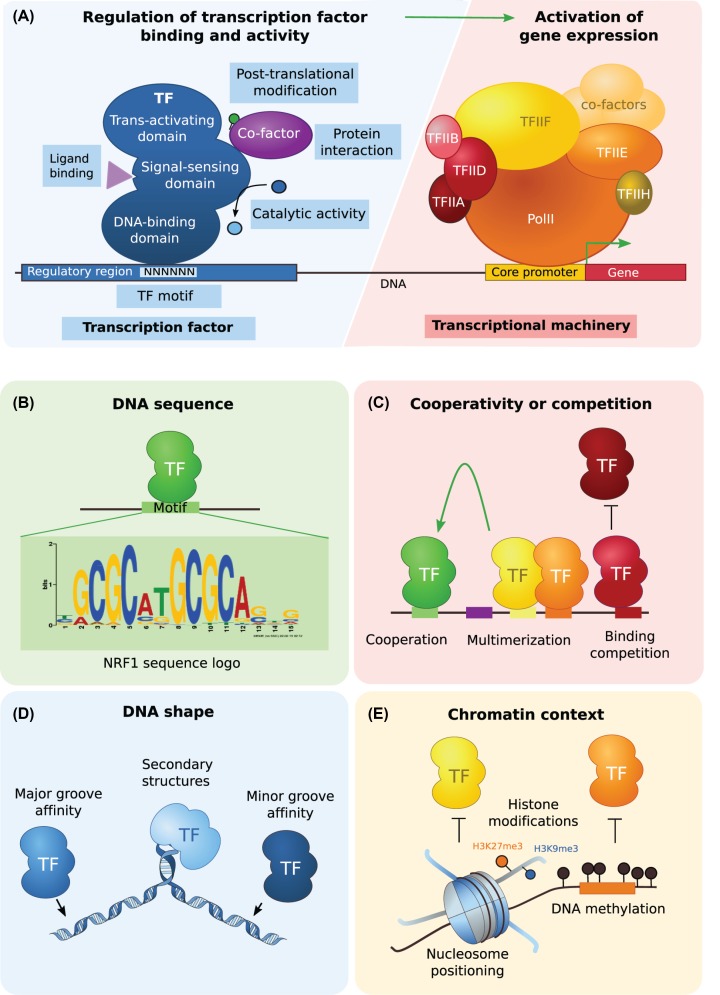
Figure 1. TF binding to DNA.
(A) TFs act as regulators of gene expression by binding to regulatory regions and recruiting the transcriptional machinery. They are composed of a DNA-binding domain that recognizes specific DNA sequence motifs, an optional signal-sensing domain that can alter TF activity after integrating signals from ligand binding, catalytic activity, protein interaction or post-translational modification, and a trans-activating domain that translates all these cellular cues into a repression or activation activity to regulate gene expression. (B) TF binding to DNA mainly relies on the recognition of specific DNA sequence motifs, the interaction with other TFs such through cooperativity or competition, the DNA shape (e.g. propeller twist, loops, rolls) and the chromatin context (e.g. nucleosome positioning, histone modifications, DNA methylation). NRF1 motif JASPAR ID: MA0596.1. Abbreviation: NRF1, nuclear respiratory factor 1.