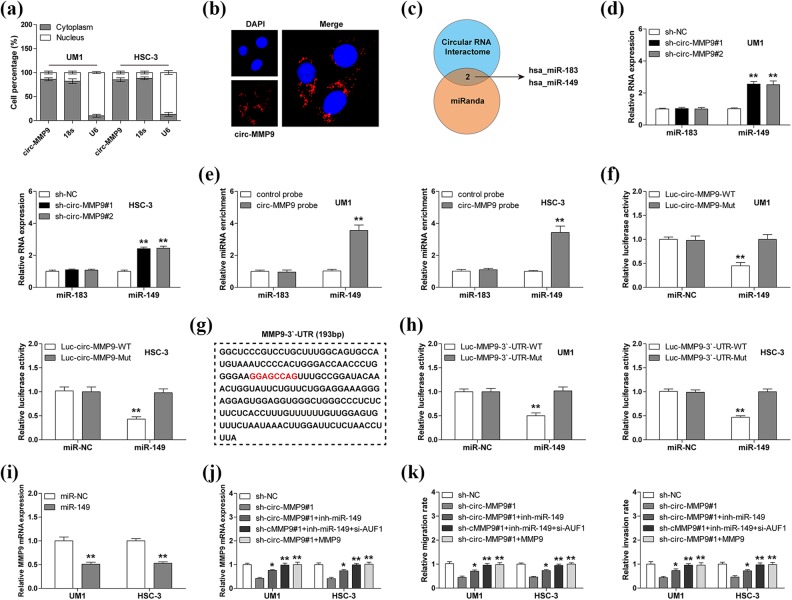
Fig 4.
Circular matrix metalloproteinase 9 (circ-MMP9) sponges miR-149 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells. (a, b) Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assays for the determination of cell sublocalization of circ-MMP9. Respectively, 18 s and U6 represented the internal references of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, and nucleus was stained by 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (c) microRNAs (miRNAs) with both circ-MMP9 and MMP9 binding sites predicted by CircInteractome and miRanda databases. (d) qRT-PCR analysis for miR-183 and miR-149 expression in circ-MMP9-depleted UM1 and HSC-3 cells. (e) RNA pull-down assay using biotin-labeled circ-MMP9 probe in UM1 and HSC-3 cells, followed by qRT-PCR analysis for miR-183 and miR-149 expression. (f) Luciferase reporter assay in UM1 and HSC-3 cells co-transfected with control or miR-149 mimics and wild-type or mutant circ-MMP9 reporter. (g) The sequence marked in red denotes miR-149 binding motif on MMP9 3′-untranslated region (UTR). (h) Luciferase reporter assay in UM1 and HSC-3 cells co-transfected with control or miR-149 mimics and wild-type or mutant MMP9 3′-UTR reporter. (i) qRT-PCR analysis for MMP9 expression in UM1 and HSC-3 cells transfected with control or miR-149 mimics. (j) qRT-PCR analysis for MMP9 expression in circ-MMP9-depleted UM1 and HSC-3 cells transfected with miR-149 inhibitors, miR-149 inhibitors+si-USF1, or MMP9 expression vector. (k) The assessment of migratory and invasive abilities of circ-MMP9-depleted UM1 and HSC-3 cells transfected with miR-149 inhibitors, miR-149 inhibitors+si-USF1, or MMP9 expression vector. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.