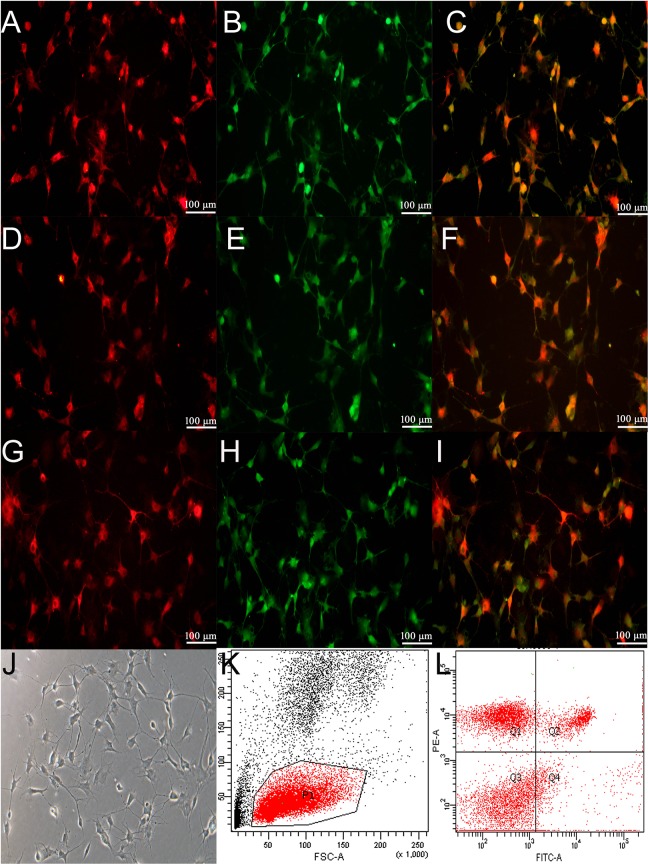
Figure 1.
Characterization of EPCs. Rat peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated by density gradient centrifugation, as described in the Materials and Methods. The endothelial characteristics were identified through the positive staining of both DiI-acetyl-LDL (A, red) and FITC-UEA-1 (B, green). The merged image of DiI-acetyl-LDL and FITC-UEA-1 is presented in C (yellow). Furthermore, EPCs were recognized through the cytoplasmic positive signals of both VEGFR-2 (D, 400 × magnification, red) and CD34 (E, 400 × magnification, green). The merged image of VEGFR2 and CD34 is presented in F (yellow). In addition, EPCs were identified with VEGFR-2 (G, 400 × magnification, red) and CD133 (H, 400 × magnification, green). The merged image of VEGFR2 and CD34 is presented in I (yellow). From the tenth day after isolation, these cells were characteristic of a monolayer (J, 400 × magnification). Abbreviations: EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; LDL, low density lipoprotein; UEA-1, ulexeuropaeus agglutinin-1; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2.