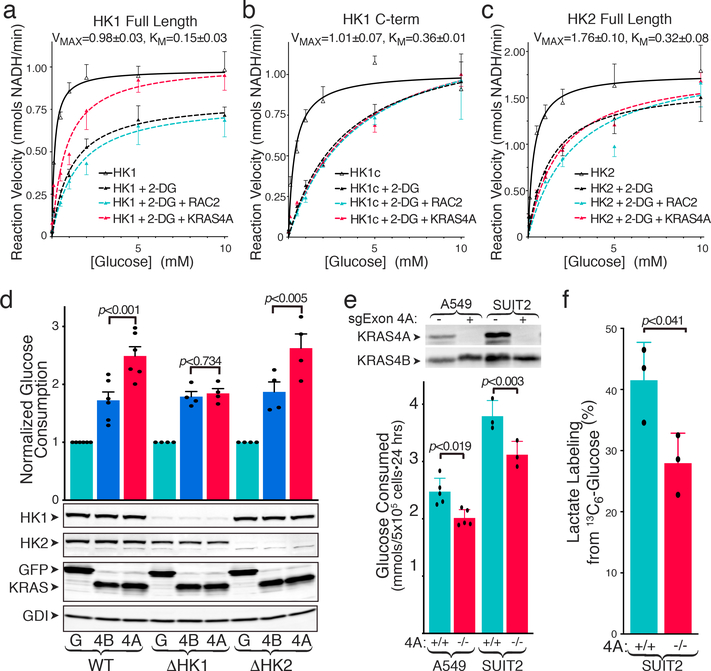
Fig. 4. |. KRAS4A increases HK1 activity in vitro and in vivo.
a-c, Activity of recombinant full-length HK1 (a), C-terminal kinase domain of HK1 (b) or full-length HK2 (c). Reaction velocity is plotted (mean±SE) as a function of glucose concentration. Velocities ±2-DG (20 mM) are shown ±addition of recombinant, GTP-loaded RAC2 or KRAS4A. Plots combine independent assays, n=4 (a) or n=3 (b,c). d, WT (n=6) or HK1- or HK2-deficient (n=4) HEK293 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged GFP, KRAS4B12V, or KRAS4A12V, and 24-h glucose consumption (mean±SE) was determined. Immunoblot shows relative expression. e, Glucose consumption (mean±SE) of parental and KRAS4A-targeted A549 (n=5) and SUIT2 (n=3) human cancer cells. f, Incorporation of 13C from glucose into lactate (mean±SE) over 15 min in SUIT2 cells ±KRAS exon 4A (n=3). Immunoblot shows absence of KRAS4A. d-f, Significance determined by two-sided student’s t-test (d-e paired; f unpaired). Growth rates of the two genotypes were equal over 24 hr assessment.