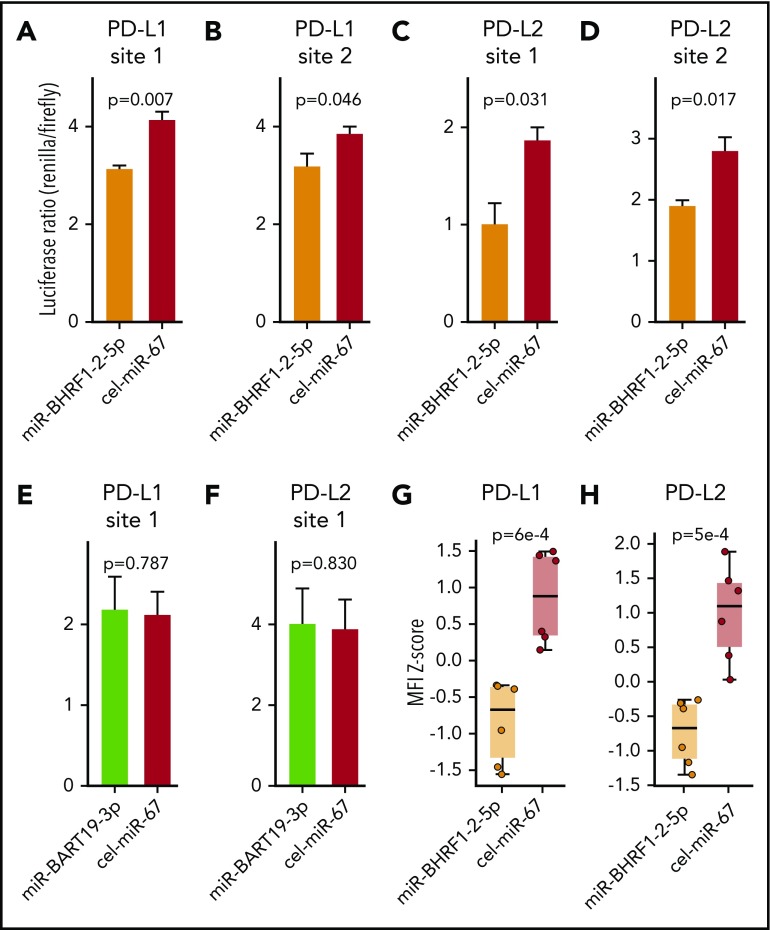
Figure 6.
EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p represses the expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 by directly binding to target sites in the 3′UTRs of PD-L1 and PD-L2 transcripts. Dual luciferase reporter assays in HEK293 cells of EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p target sites predicted in the 3′UTR of PD-L1, PD-L1 site 1 (A) and PD-L1 site 2 (B), and in the 3′UTR of PD-L2, PD-L2 site 1 (C) and PD-L2 site 2 (D). Luciferase reporter assays were also performed for EBV miR-BART19-3p target sites predicted in the 3′UTR of PD-L1, PD-L1 site 1 (E) and PD-L2 site 2 (F). Renilla luciferase is the reporter gene with the candidate miR binding site cloned in its 3′UTR, and firefly luciferase is used as normalizer constitutively expressed by the same vector. A decrease in the luciferase ratio is indicative of an effective functional binding of the miR to its target site. All 4 EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p target sites contribute to the downregulation of Renilla luciferase by synthetic EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p mimic treatment compared with a control miR mimic based on Caenorhabditis elegans miR-67 (cel-miR-67), whereas EBV miR-BART19-3p mimics have no significant effect over the predicted binding sites in the 3′UTRs of PD-L1 and PD-L2. EBV WIL LCLs were treated with EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p or cel-miR-67 (control) mimics, and PD-L1 and PD-L2 protein levels were quantified by flow cytometry. Results of 2 independent experiments were combined to quantify PD-L1 (G) and PD-L2 (H) protein levels at 8 and 24 hours after miR mimic treatment. Welch’s 2-sample t test was used for statistical analysis. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.