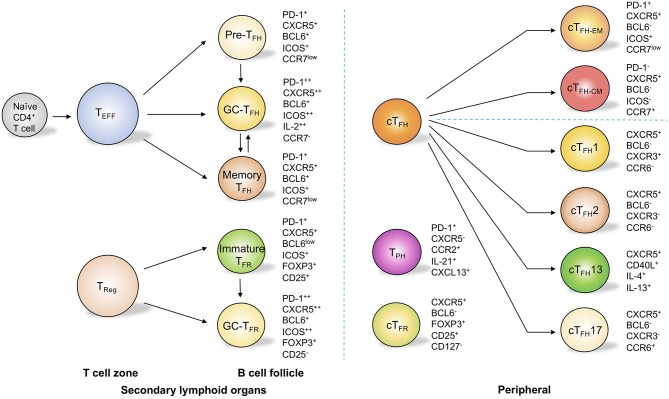
Figure 1.
TFH cell and related subsets in secondary lymph organs and in peripheral circulation. In secondary lymphoid organs, T follicular helper (TFH) cells are composed of subsets with distinct phenotypes. These subsets include pre-TFH cells, germinal center (GC) TFH cells, and memory TFH cells. Through the upregulation of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and CXC-chemokine receptor 5 (CXCR5), regulatory T (Treg) cells migrate into B cell follicles and become immature T follicular regulatory (TFR) cells and germinal center TFR cells. In the peripheral circulation, circulating TFH (cTFH) cells can be categorized into effector memory (cTFH−EM) cells and central memory (cTFH−CM) cells on the basis of the expression of PD-1 and CC-chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7). cTFH cells can also be sub-grouped into cTFH1, cTFH2, cTFH13, and cTFH17 cells on the basis of the differential expression of CXCR3 and CCR6 as well as the secretion of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13. Circulating TFR cells are similar to Treg cells but express CXCR5. Notably, T peripheral helper (TPH) cells do not express CXCR5 but can produce IL-21 and CXCL13, which allows them to provide help to B cells.