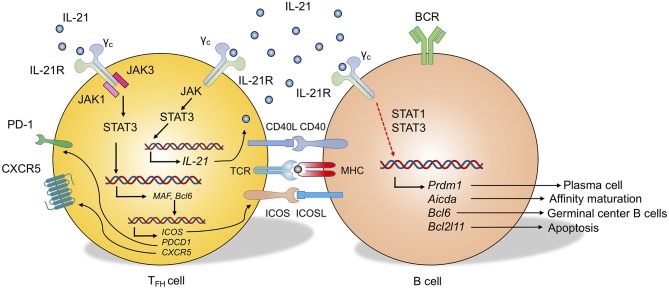
Figure 2.
Role of IL-21 in TFH cell and B cell differentiation. IL-21 binds to the IL-21 receptor (IL-21R), which dimerizes with the common cytokine receptor-γ chain (γc) to form the IL-21R complex. In TFH cells, IL-21 signaling activates Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) and JAK3 to induce phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3, also STAT1 and STAT5 to some extent). STAT3 protein translocates into the cell nucleus and regulates the transcription of target genes, including IL-21, Maf, and Bcl6. This regulation leads to the autocrine IL-21 by TFH cells and the transcriptional program that upregulates genes encoding CXCR5, ICOS, and PD-1. In B cells, at least partially through STAT1 and STAT3, IL-21 signaling can regulate the gene expression of Prdm1 (Plasma cell differentiation), Acida (Affinity maturation), Bcl6 (Germinal center B cells), and Bcl2l11 (B cell apoptosis) which leads to the differentiation of B cells to multiple directions.