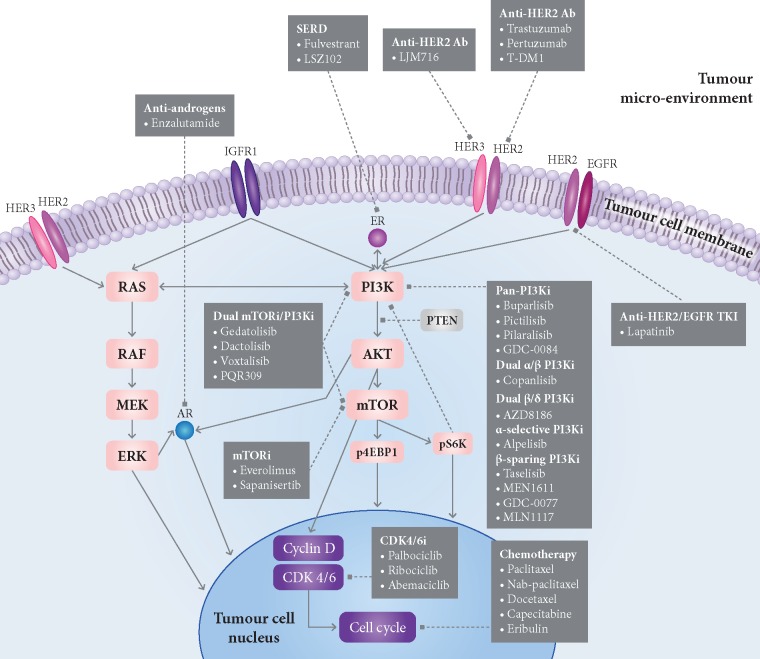
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of resistance to PI3K inhibitors in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer and current and future drug combination strategies involving PI3K inhibitors. In PIK3CA-mutated breast tumours, resistance to PI3K inhibitors can be mediated by multiple mechanisms, including activation of alternative pathways that drive cell proliferation (e.g. RAS/MEK/ERK pathway, ER pathway, or HER2 pathway); by signalling via other PI3K isoforms when a specific subunit is blocked; by activation of downstream effectors in the PI3K pathway such as AKT and mTOR; by loss of regulators of PI3K signalling such as PTEN; or by epigenomic crosstalk between PI3K and ER pathways, resulting in upregulation of ER-dependent transcription. Ab, monoclonal antibody; AR, androgen receptor; CDK4/6i, CDK4/6 inhibitors; ER, estrogen receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; HER3, human epidermal growth factor receptor 3; IGFR1, insulin growth factor receptor 1; mTOR, mTOR inhibitors; PI3Ki, PI3K inhibitors; SERD, selective estrogen receptor degraders; T-DM1, ado-trastuzumab emtansine; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Dashed arrows, inhibitory function; bold arrows, activation function. Note: within each drug class, we have only included compounds that have been or that are currently being tested in combination with PI3K inhibitors in clinical trials (see Tables 2 and 3 for more details).