Figure 1.
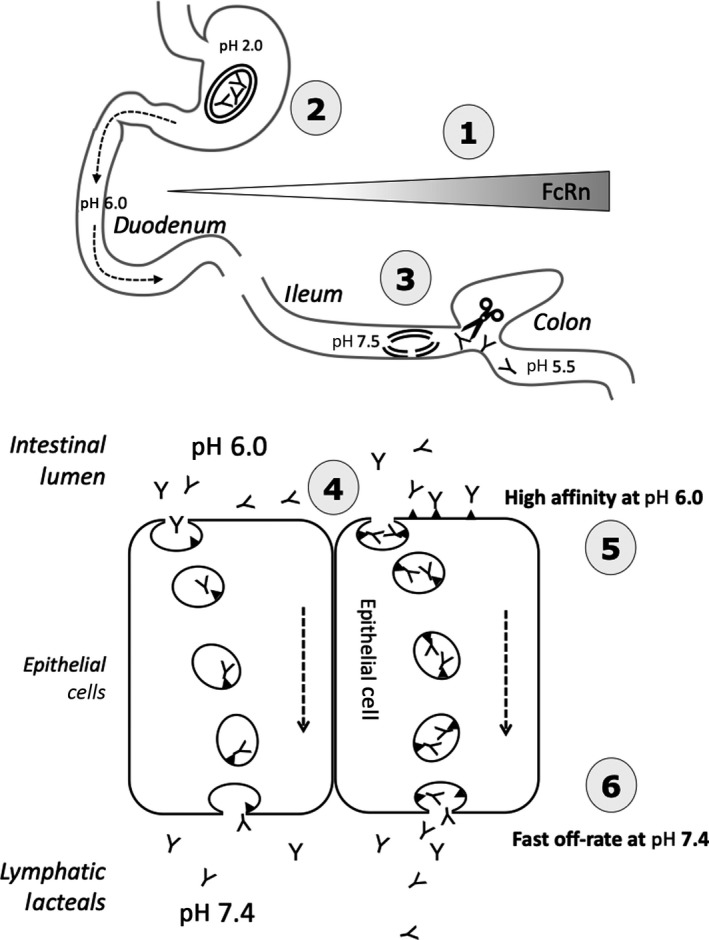
Working model used to establish the pharmacology of intestinal FcRn. This was used for the selection of a mAb in order to assess oral bioavailability in a 10 week dosing study in cynomolgus monkeys. 1. In human, FcRn expression increasing proximal‐distal gradient in the intestine. 2. Lyophilized mAb stable and loaded in sufficient amounts for dosing into enteric‐coated capsule protected from dissolution at low pH. 3. Enteric coating undergoes rapid dissolution at pH 7.5 in the terminal ileum to release mAbs that resist luminal proteases. 4. mAbs reach the apical surface of enterocytes and are limited by the rate of pinocytosis, unless there is IgG‐FcRn receptor surface binding. 5. Low pH favors mAbs binding at the apical cell surface or within the endosome, where they are trafficked to the basolateral side. 6. mAbs must have a fast off‐rate at pH 7.4 to reach lymphatic lacteals and eventually the systemic circulation. ▼, FcRn; Y, mAb; double lined oval, enteric coated capsule
