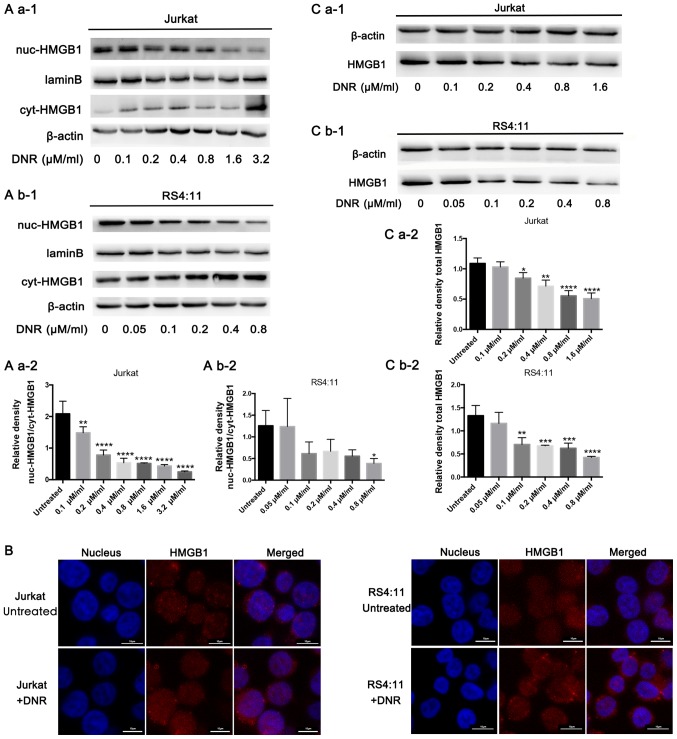
Figure 2.
HMGB1 translocation is associated with chemotherapeutic drug-induced autophagy. (A) Cell lysates were separated into cytosolic and nuclear fractions. Cytosolic and nuclear HMGB1 levels were assayed via western blotting. β-actin was used as a loading control to detect the expression of cytoplasmic protein, while laminB was used to detect the expression of nuclear protein. Quantified data are presented [(nuc-HMGB1/laminB)/(cyt-HMGB1/β-actin)]. (a-1) Western blot diagram of Jurkat cells. (a-2) nuc-HMGB1/cyt-HMGB1 quantitative data of Jurkat cells. (b-1) Western blot diagram of RS4:11 cells. (b-2) nuc-HMGB1/cyt-HMGB1 quantitative data of RS4:11 cells. (B) Intracellular HMGB1 was stained via indirect immunofluorescence and analysed under a confocal microscope to detect the location of HMGB1 (HMGB1, Cy3 staining; nucleus, DAPI staining). (C) Cell lysates were subjected to western blotting to detect HMGB1 expression. β-actin was used as a loading control. Quantified data are presented (HGMB1/β-actin). Data are the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. (a-1) Western blot diagram of Jurkat cells. (a-2) Total HMGB1 quantitative data of Jurkat cells. (b-1) Western blot diagram of RS4:11 cells. (b-2) Total HMGB1 quantitative data of RS4:11 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001, compared with the untreated group. HMGB1, high mobility group box protein 1; DNR, daunorubicin; Cyt, cytoplasm; Nuc, nucleus.