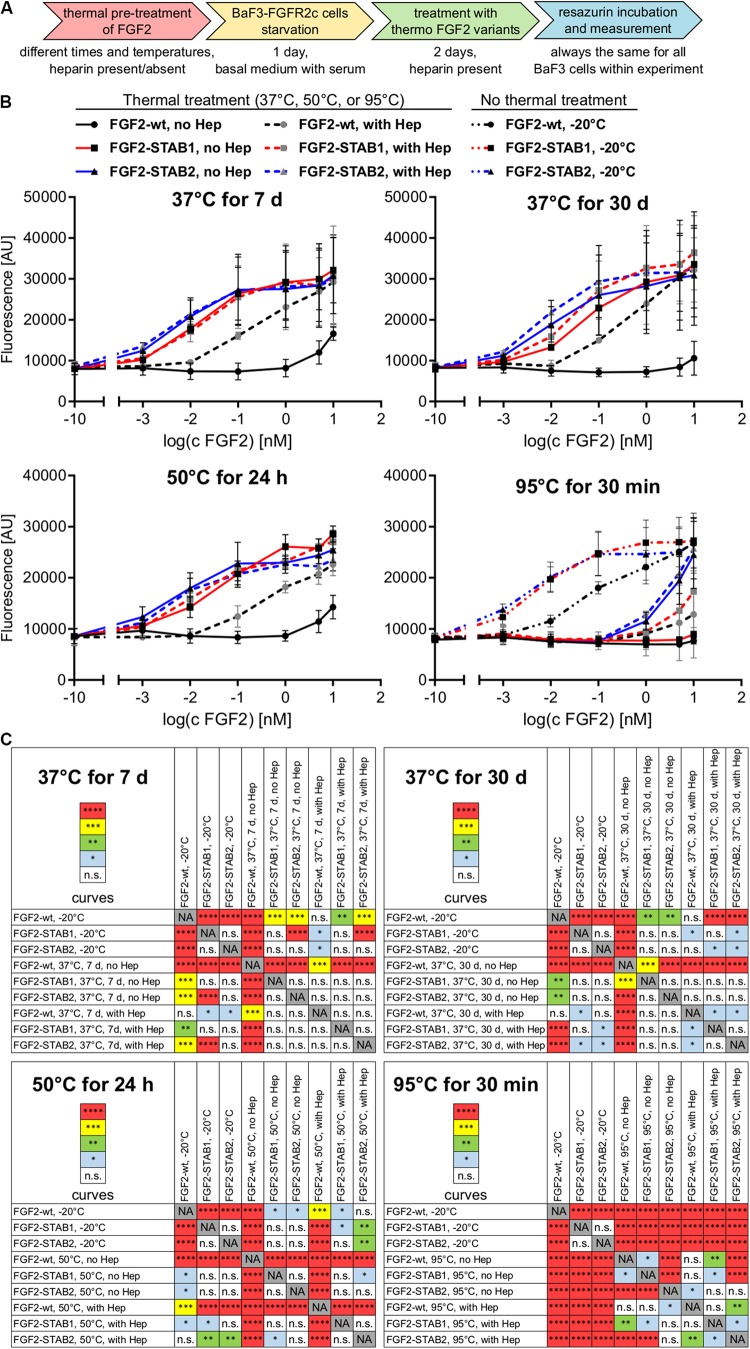
FIGURE 2.
FGF2-STABs show increased thermal stability. (A–C) Thermostability testing using proliferation assay of BaF3-FGFR2c cells. (A) Experimental design scheme. FGF2 variants were exposed to 37, 50, or 95°C in the presence (2 μg/ml heparin; with Hep) or absence of heparin (no Hep) for the times indicated, or not thermally treated at all but stored at −20°C, and then used to treat the BaF3-FGFR2c cells. BaF3-FGFR2c cells were seeded in basal medium containing serum and treated with FGF2 variants in the presence of heparin (2 μg/ml) for 4 days. (B) The line plots show resorufin fluorescence, measured after 4 days of culture with FGF2 variants, as mean ± SD, n = 2–3. For visual clarity, the plots for thermally non-treated FGF2 variants (−20°C) are shown only in the plots with 95°C-treated variants, otherwise they were too much overlapping with the curves in graphs of other thermal treatments. (C) The color maps show results of statistical comparison of whole curves of FGF2 variants after thermal treatment. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; n.s., not significant (two-way ANOVA).