Figure 1.
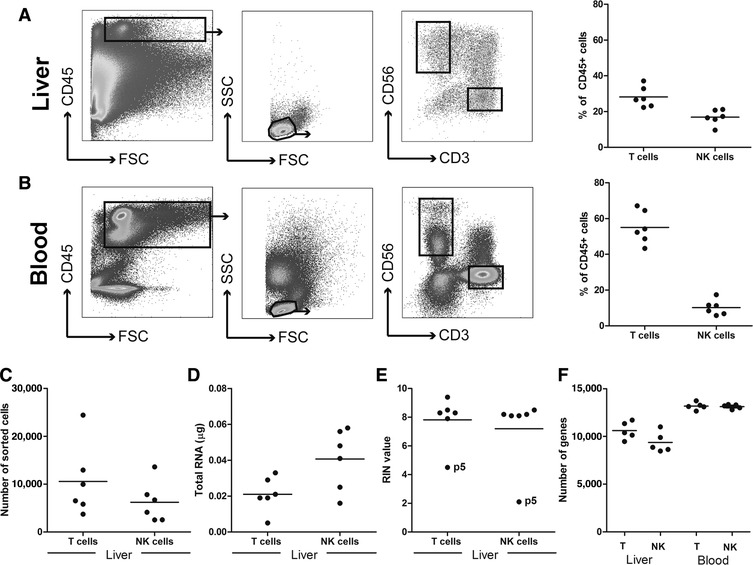
Description of the gating strategy and quality control steps for isolated mRNA derived from liver immune cell populations. (A) FACS plots showing the gating strategies for liver T cells (CD45+CD3+CD56‐ lymphocytes), and NK cells (CD45+CD3‐CD56+ lymphocytes) of 6 chronic HBV patients treated with nucleotide analogs. The panel on the right‐hand side shows the T cell and NK cell frequencies of total intrahepatic CD45+ cells. (B) The gating strategy for peripheral blood T cells and NK cells, including the T cell and NK cell frequencies of the total blood CD45+ population (right panel). (C) The absolute number of intrahepatic T and NK cells sorted by flow cytometry. (D) The total amount of RNA obtained from the sorted cells. (E) The RNA integrity number (RIN value) of the RNA samples. (F) The total number of unique genes identified in T cells and NK cells from the 5 liver biopsies passing quality control, in comparison to blood‐derived T and NK cells
