Fig 2. Grouped reaction times per condition, across subjects (n = 27).
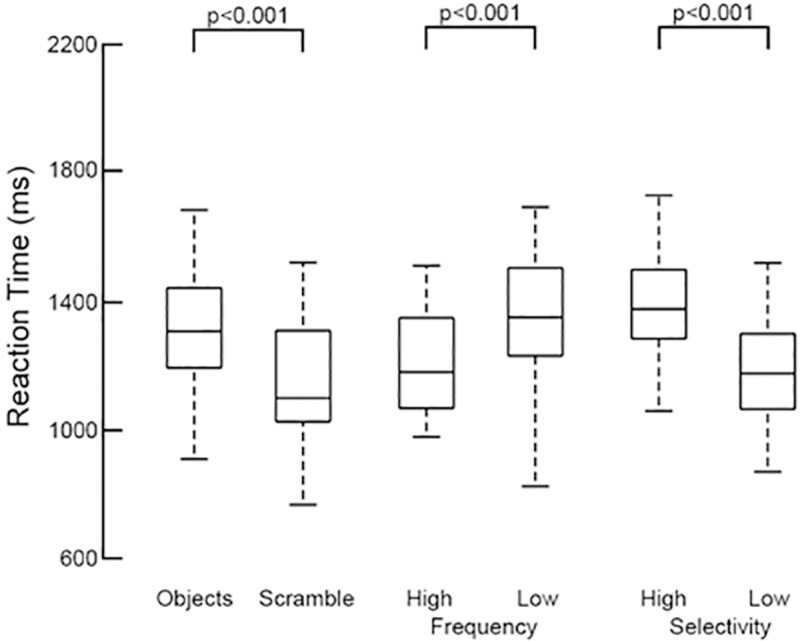
Using the audio recording, each patient’s reaction time was calculated based on the onset of their verbal response. Across the group, object naming had significantly higher latency than scrambled naming (p<0.001, two-sided, paired t-test. High-frequency objects had a significantly shorter latency than low-frequency words (p<0.001), and high-selectivity objects had higher latency than low-selectivity objects (p<0.001).
