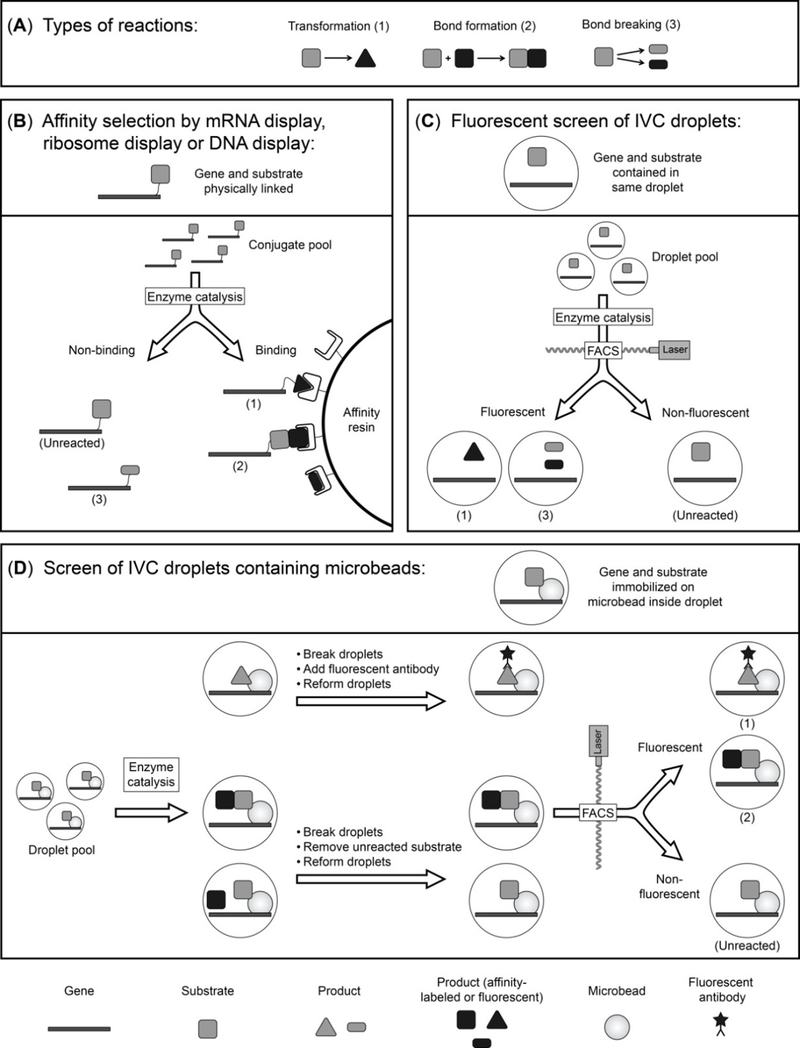
Fig. 2.
Isolation of enzymatic activities using in vitro technologies. (A) Types of enzymatic activities that can be evolved using in vitro approaches. (B) Affinity selection of physically linked gene-substrate/product conjugates. The enzyme itself is also linked to the gene-substrate complex, but is omitted from the figure for improved clarity. (C) Screen of IVC droplets that become fluorescent as a result of catalysis by the enzyme (not shown) contained in same compartment. Separation is achieved through fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) or microfluidics. (D) Screen for enzyme catalysis by FACS of IVC droplets containing microbeads. The enzyme contained in each compartment is not shown to improve clarity. Numbers in brackets refer to the type of activity as shown in (A).