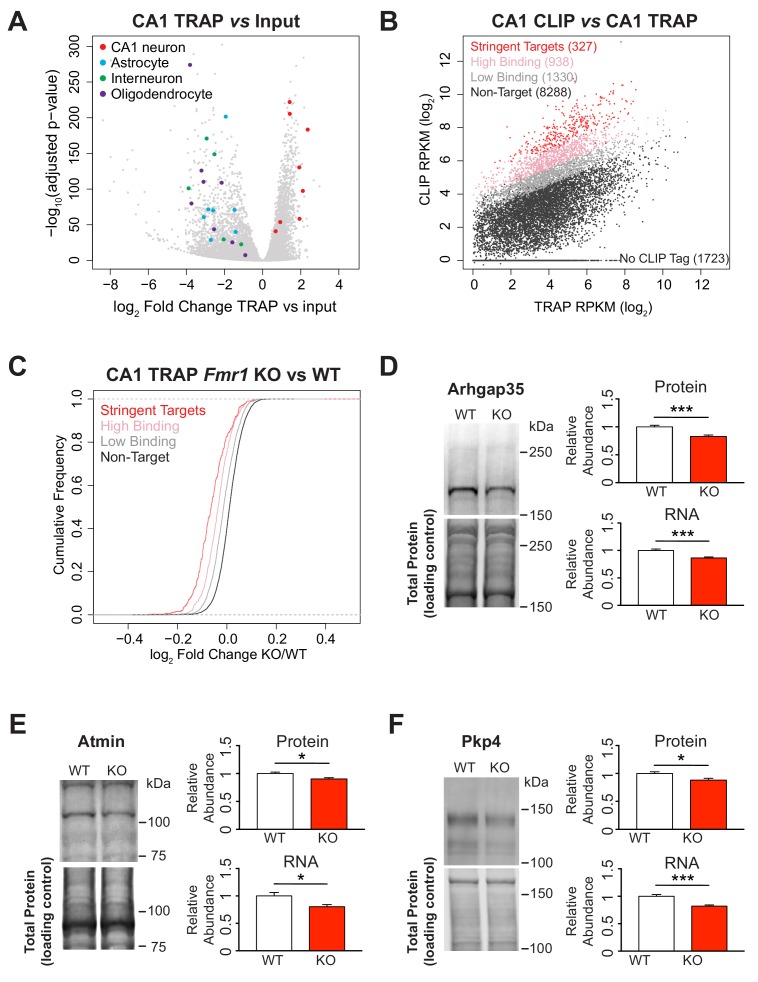
Figure 2. Identification of FMRP targets and CA1 neuron specific TRAP in the Fmr1 KO.
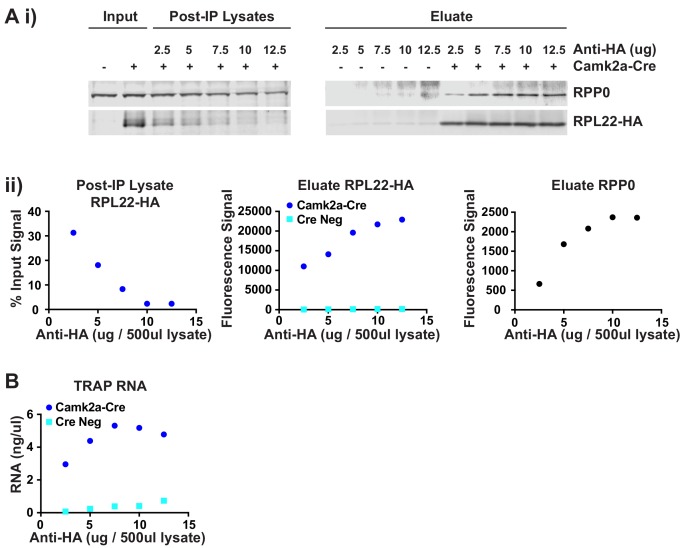
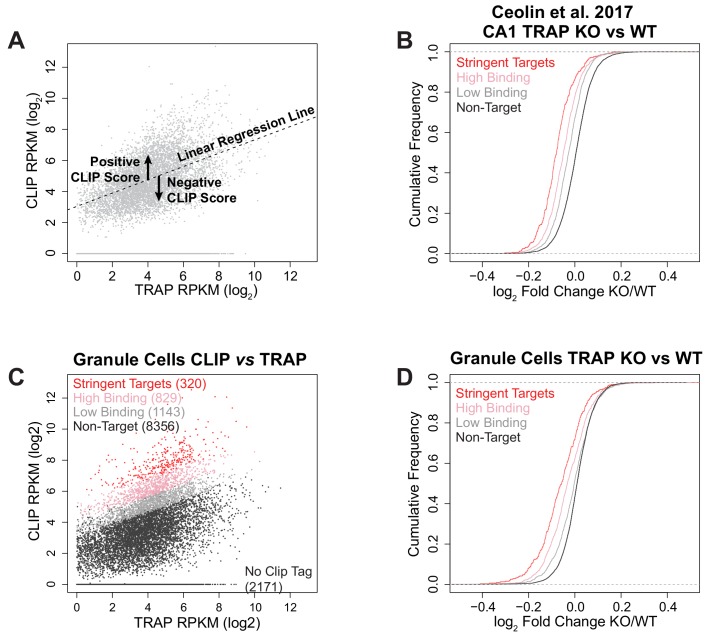
(A) Immunoprecipitation of ribosome associated RNA from CA1 neurons from WT and Fmr1 KO animals. Differential analysis of counts per gene from TRAP RNA compared to input RNA showing fold change and statistical significance as determined by DESeq2. CA1 markers (Wfs1, Pou3f1, Nov, Man1a, Mpped1, Cds1, Fibcd1, Satb2) are enriched in the IP whereas markers for other cell types are depleted (Astrocytes: Slc1a2, Gjb6, Gfap, Slc1a3, Aqp4, Aldoc, Aldh1l1; Interneurons: Slc6a1, Slc32a1, Gad1, Gad2, Pvalb; Oligodendrocytes: Cnp, Mog, Mag, Olig2, Olig1, Mobp, Mbp, Mal). (B) FMRP targets were defined by normalizing CLIP tag density across the coding region to the relative abundance of the transcript as measured by TRAP. A CLIP score per transcript was calculated independently for each replicate of the CLIP experiment. Stringent targets were defined as those with a CLIP score > 2 in every replicate, targets with high binding were defined as those with an average CLIP score > 1 and targets with low binding were defined as those with an average CLIP score between 0 and 1. Scatter plot of average density of CLIP tags across the coding region (CLIP RPKM) vs transcript abundance calculated as TRAP read density across the full transcript (TRAP RPKM). Targets of each subclass are highlighted in the plot and the number of genes within each subclass is indicated. (C) FMRP targets are down-regulated in the Fmr1 KO, with the magnitude of the effect being proportional to the amount of FMRP binding. Cumulative density function plots of the log2 fold change between Fmr1 KO TRAP and WT TRAP for each FMRP target subclass. All subclasses have a significant shift compared to the unbound group (Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, p-value<2.2×10−16 for all pairwise comparisons) and there are also significant differences between each subclass (stringent binding vs high binding: p-value=5.78×10−9; high binding vs low binding: p-value<2.2×10−16). (D–F) Quantitative western blot and PCR validation of TRAP results. Protein and RNA levels of the FMRP targets Arhgap35 (D), Atmin (E) and Pkp4 (F) are decreased in hippocampal lysates from Fmr1 KO mice relative to WT. A representative western blot is shown for one pair of WT and KO littermates. Western blots were normalized to total protein per lane visualized with REVERT total protein stain. qPCR data was normalized to Gapdh, Actin and Hprt housekeeping genes. Data are from 6 to 9 animals per genotype and mean ± SEM is shown. p-values were calculated using Student’s t-test (*p<0.05, ***p<0.001).