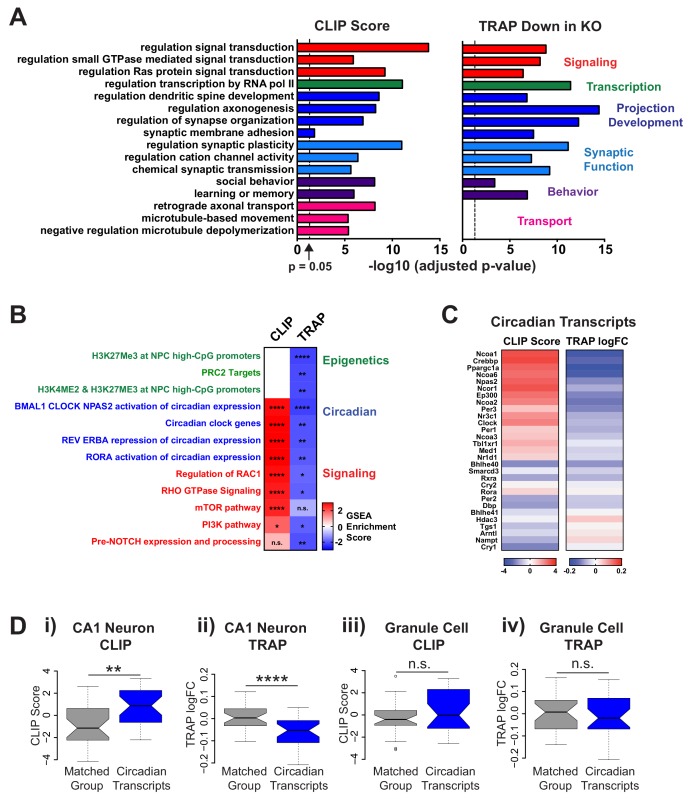
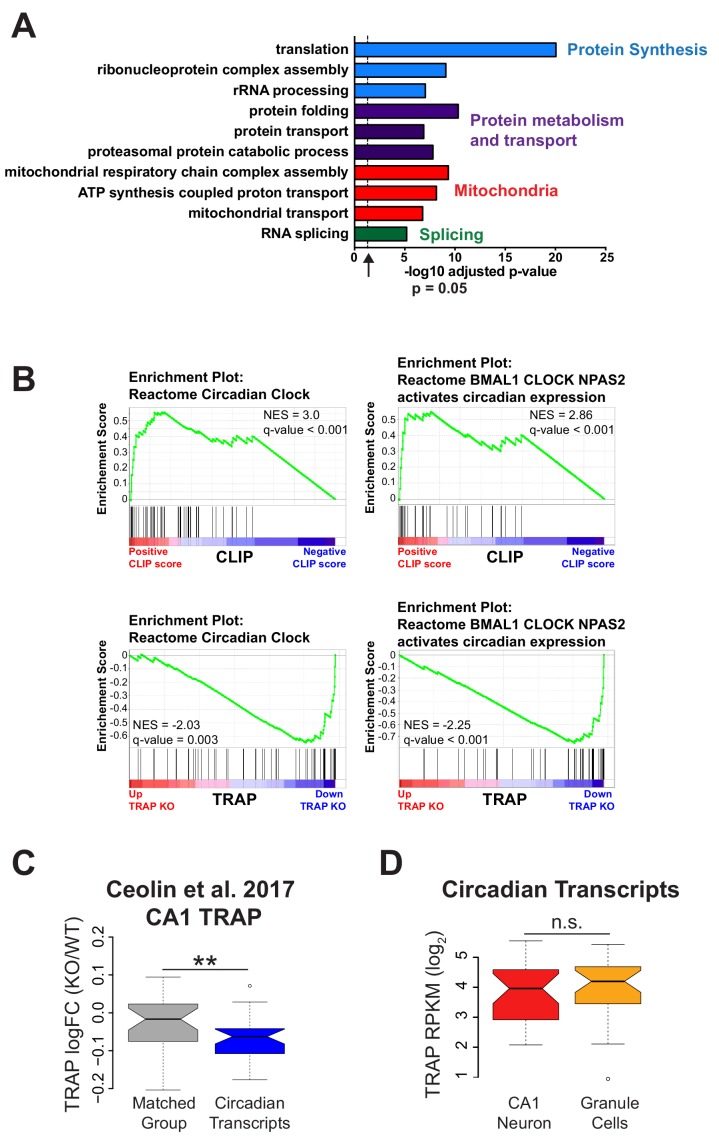
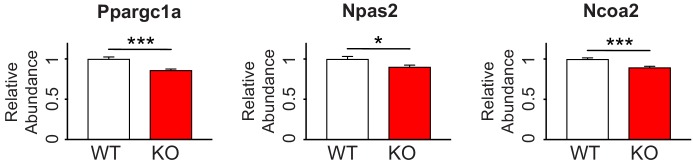
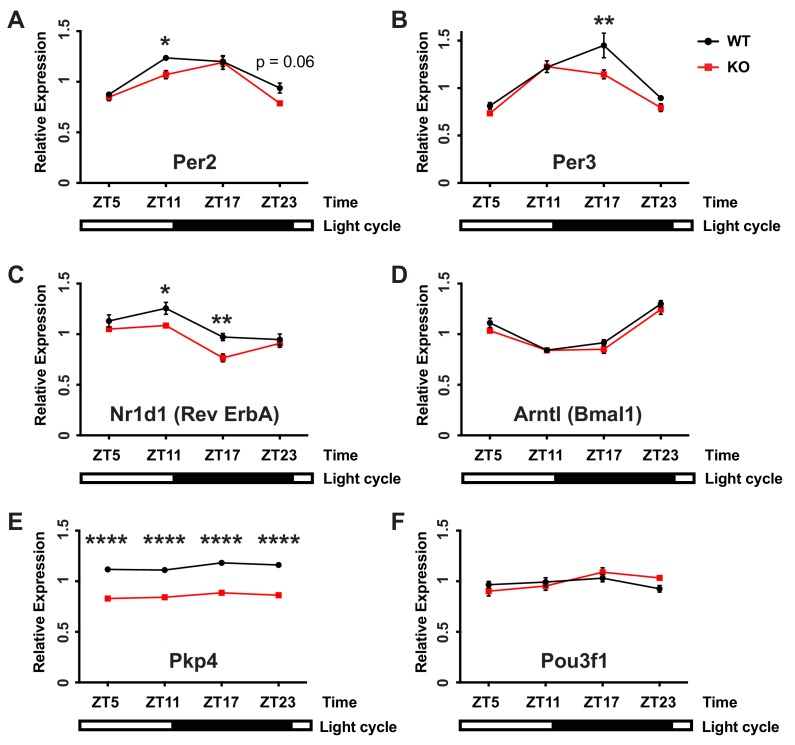
Figure 4. FMRP targets genes involved in neuronal function and circadian rhythm in CA1 neurons.
(A) Selected results from gene ontology analysis of CA1 transcriptome ranked by FMRP binding (CLIP Score) or negative log fold change Fmr1 KO vs WT TRAP. (B) Selected results from gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of the same ranked data sets. Heatmap represents normalized enrichment score (NES) with FDR values indicated (* FDR < 0.05; ** FDR < 0.01, *** FDR < 0.001, **** FDR < 0.0001, n.s. not significant). The NES reflects the degree to which a gene set is overrepresented at the top or bottom of a ranked list of genes normalized for differences in gene set sizes. (C) Heatmaps of CLIP score and log2 fold change Fmr1 KO vs WT TRAP for transcripts in the ‘BMAL1 CLOCK NPAS2 activation of circadian expression’ gene set from the Reactome database (Fabregat et al., 2018). (D) Circadian genes encode transcripts that are specifically bound and regulated by FMRP in CA1 neurons. Distribution of CLIP score (i, iii) and log2 fold change Fmr1 KO vs WT TRAP (ii, iv) for circadian genes in the ‘BMAL1 CLOCK NPAS2 activation of circadian expression’ Reactome gene set are shown relative to a set of randomly selected genes from the relevant transcriptome matched both for the number of genes represented and transcript length (Matched Group). Data are show for CA1 neurons (i, ii) and cerebellar granule cells (iii, iv). P-values were calculated using the Wilcoxon rank sum test (**p<0.01, ****p<0.0001, n.s. not significant).