Fig. 1. Role of EF-G in mRNA reading frame maintenance.
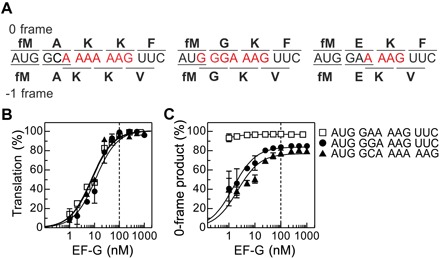
(A) Coding sequences of the mRNAs used in this work. The potential slippery sequence is colored red. Amino acids incorporated in 0 and −1 frame are indicated above and below the respective coding sequences. (B) Dependence of translation on EF-G concentration. Products were analyzed after 5 min of translation. Translation efficiency was normalized by setting the end level to 100% for better comparison between mRNAs. Lines are visual guides. The dashed line indicates the concentration at which ribosomes and EF-G are equimolar. Error bars represent SD of three experiments (n = 3). (C) Fraction of the 0-frame peptide depending on the EF-G concentration. Error bars represent SD of three experiments (n = 3).
