Fig. 1. Heart and skeletal muscle conditional knockout of mouse Mtif3 causes cardiomyopathy.
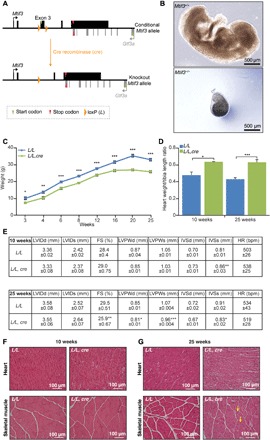
(A) Schematic showing the homologous recombination at the Mtif3 locus to generate conditional knockout mice. LoxP sites were introduced to allow the deletion of exon 3 by Cre recombinase. (B) Development of embryos of Mtif3+/+ and constitutive Mtif3−/− mice at embryonic day 8.5 (E8.5). (C) Weight differences between control (L/L) and knockout (L/L, cre) mice from 3 to 25 weeks of age. (D) Heart weight–to–tibia length ratio in control (L/L) and knockout (L/L, cre) mice at 10 and 25 weeks. (E) Echocardiographic parameters for control (L/L), and knockout (L/L, cre), 10- and 25-week-old mice. LVIDd, left ventricular end diastolic diameter; LVIDs, left ventricular end systolic diameter; FS, fractional shortening; LVPWd, left ventricular posterior wall in diastole; LVPWs, left ventricular posterior wall in systole; IVSd, intraventricular septum in diastole; IVSs, intraventricular septum in systole; HR, heart rate. (F) Heart and skeletal muscle sections cut to 5-μm thickness from 10-week-old and (G) 25-week-old L/L and L/L, cre mice were stained with H&E; yellow arrows show centralized nuclei in the skeletal muscle. Scale bars, 100 μm. All values are means ± SEM of n = 5. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t test.
