Figure 1.
Temporal Changes of Protein Synthesis and Accumulation in the Growing Chloroplast during the Light Phase of the Diel Cycle.
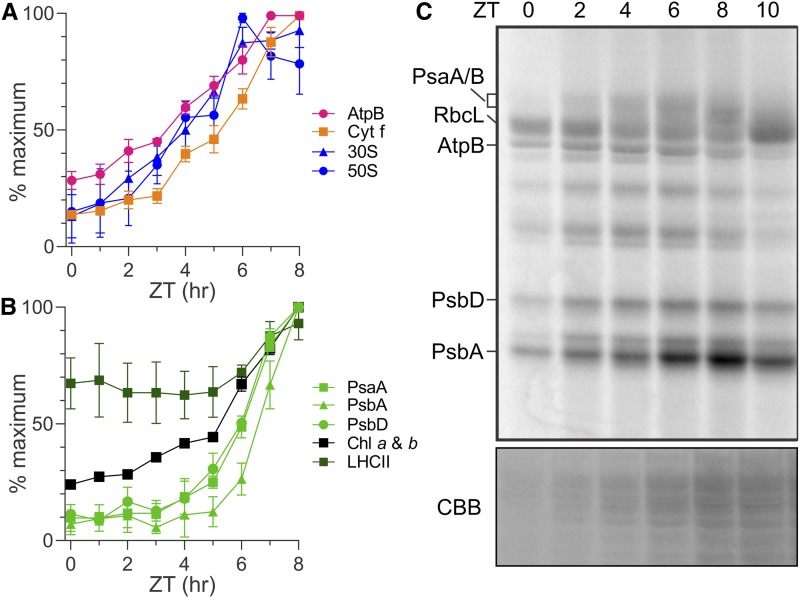
(A) and (B) Results of immunoblot analyses of total protein samples from ZT time points in the ZT0-ZT8 interval of the light phase reveal the relative levels of marker proteins (parentheses) of the following complexes: ATP synthase (AtpB), Cytb6f (Cytf), and the 30S and 50S subunits of the chloroplastic ribosome (S-21 and L7/L12, respectively; [A]) and PSI (PsaA), PSII (PsbA and PsbD), the LHCII proteins, and chlorophyll (B). Results are from three biological replicates using independent cultures. Error bars indicate 1 se. Identical protein samples were used for all analyses in each panel. Immunoblots from one replicate are shown in Supplemental Figure 2A. Supplemental Figures 2B and 2C show the same plots as in (A) and (B), respectively, but with all three data points for each ZT time point.
(C) Protein synthesis rates in the chloroplast are revealed by 10-min in vivo pulse 35S labeling of PsaA/B, AtpB, PsbD, and PsbA. Also indicated is the 35S-labeled large subunit of Rubisco (RbcL). Preferentially elevated rates of PsbA synthesis for the PSII damage-repair cycle were detected in the ZT6-ZT8 interval. The doublet bands of PsbD represent phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms (Herrin et al., 1992). Cycloheximide inhibited cytoplasmic ribosomes to reveal products of chloroplastic ribosomes. A portion of the gel with proteins was stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB).