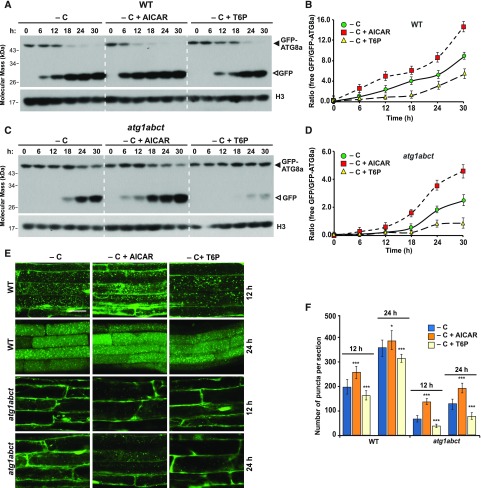
Figure 8.
SnRK1 Is Essential for the Autophagy Induced by Prolonged Fixed-Carbon Starvation.
(A) and (C) Immunoblot detection of the free GFP released during the autophagic degradation of GFP-ATG8a reporter in the wild type and the atg1abct mutant before and after exposure to AICAR or T6P. One-week-old seedlings expressing GFP-ATG8a were exposed to sucrose-deficient liquid medium and darkness with the addition of 10 mM AICAR or 0.1 mM T6P for the indicated times. Immunoblot analysis of total seedling extracts was performed as in Figure 2A.
(B) and (D) Quantification of the free GFP:GFP fusion ratio of the GFP-ATG8a reporter in (A) and (C), respectively. Levels of free GFP and the GFP fusion were determined by densitometric scans of the immunoblots. Each data point represents the mean ± sd of three independent biological replicates.
(E) The effect of AICAR and T6P treatments on the deposition of autophagic bodies inside the vacuole. Six-day-old seedlings expressing GFP-ATG8a were exposed for 12 or 24 h to sucrose-deficient liquid medium containing 1 μM ConA with the addition of 10 mM AICAR or 0.1 mM T6P added to the medium before confocal fluorescence microscopic analysis of root cells. Bar = 10 μm.
(F) Numbers of puncta per section in the root cells of the wild-type and atg1abct seedlings used in (E). ***, P < 0.01 and *, P < 0.05 indicate values that are statistically different from respective untreated controls as determined using Student’s t test; n = 30 sections from three independent experiments per genotype. Error bars represent sd.