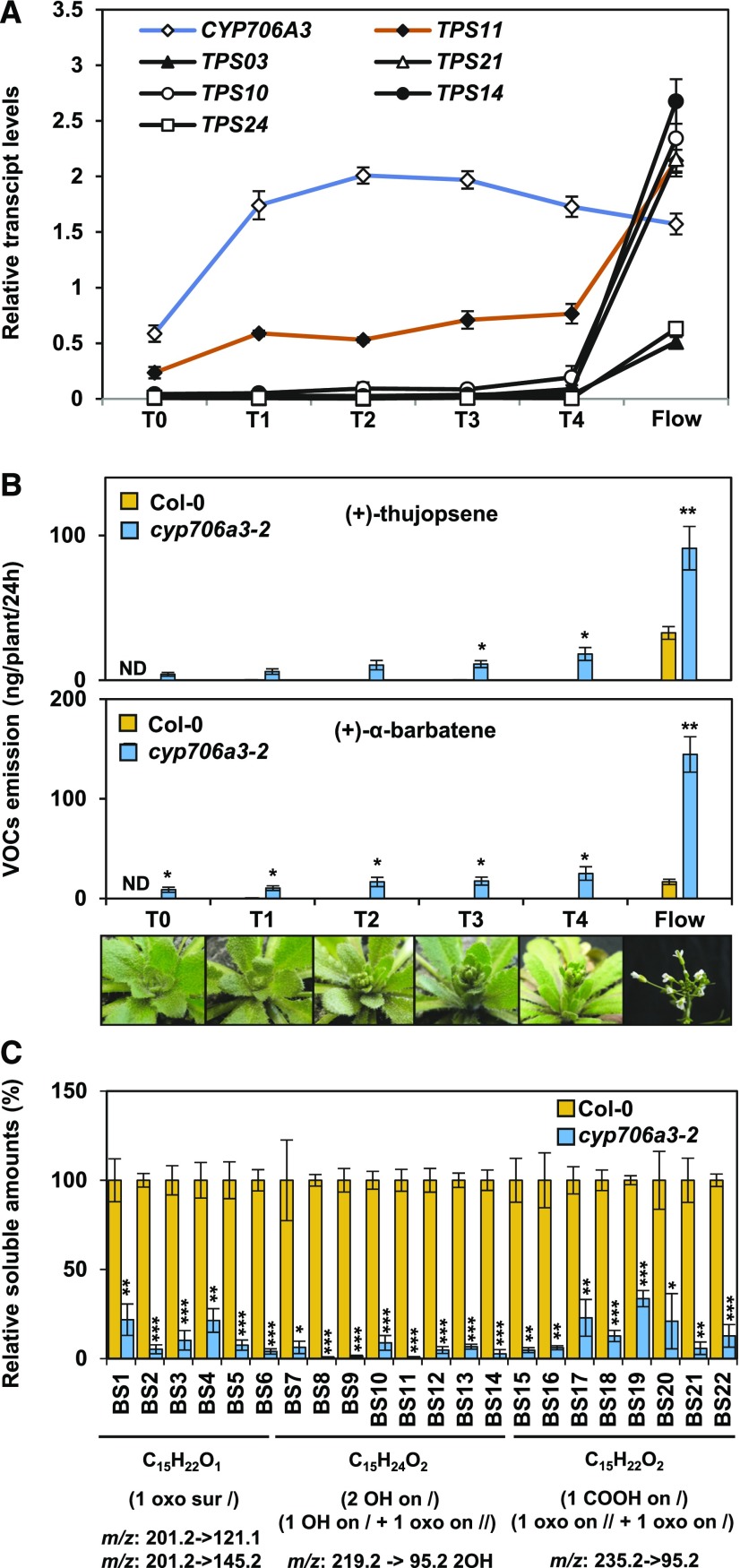
Figure 8.
The TPS11/CYP706A3 Cluster Is Active in Developing Floral Buds.
(A) Relative expression of CYP706A3 and of major flower-expressed terpene synthase genes (Figure 1) during floral transition and inflorescence development evaluated by RT-qPCR.
(B) Quantification of (+)-thujopsene (top) and (+)-α-barbatene (bottom) emission from wild-type and cyp706a3-2 mutant plants at the same development stages as in (A). VOCs were collected for 24 h from four plants per sample at the six stages of flower development shown in the photographs below from floral transition (T0) to opened inflorescence (Flow). T indicates the different transition phases.
(C) LC-MS/MS quantification of soluble sesquiterpene oxides identified in methanol extracts of stage T4 buds from wild-type and cyp706a3-2 mutant plants (as described in Figure 7). For each compound, specific MS/MS transitions used are indicated, as well as expected raw formulae. Representative chromatograms and identification of the numbered sesquiterpene oxides are shown in Supplemental Figure 16. BS, bud soluble compounds. Data in (B) are given as means ± se (n = 4 individual plants). Data in (A) and (C) are given as means ± se of three biological replicates (pooled inflorescences from individual plants). Statistically significant differences relative to Col-0 are indicated (two-tailed Student’s t test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). Statistics can be found in Supplemental Data Set 2.