Figure-5.
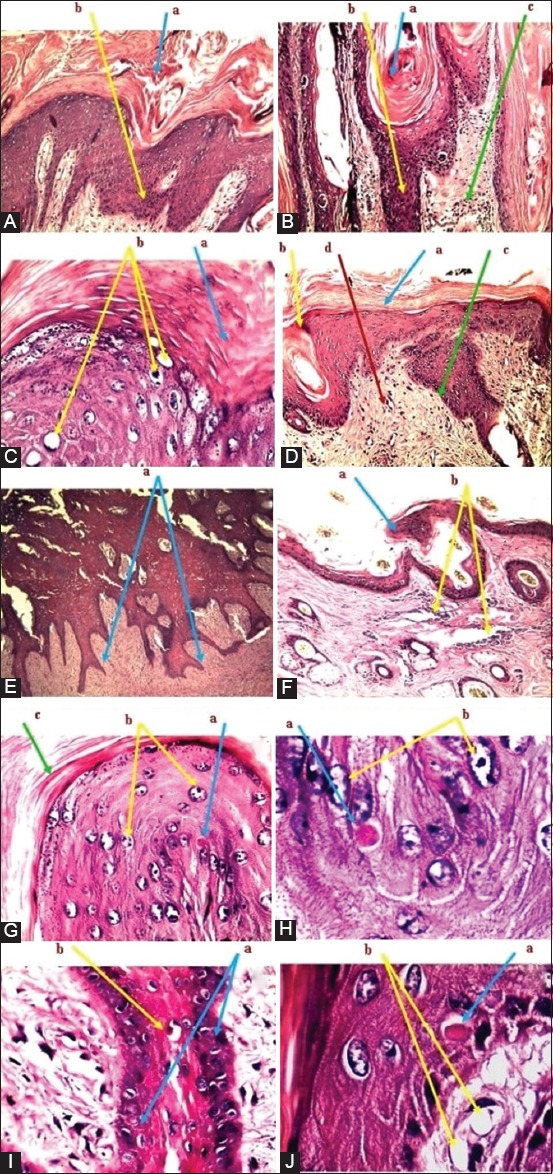
Histopathological analysis of skin nodular lesions. (A): (a) Hyperkeratosis in the epidermis. (b) Hyperplasia of stratum basale. (B): (a) Hyperkeratosis. (b) Hyperplasia. (c) Inflammatory cell infiltration. (C): (a) Hyperkeratosis. (b) Vacuolation with swelling of granulocytes. (D): (a) Hyperkeratosis. (b) Acanthosis. (c) Hyperplasia (d) Inflammatory cell infiltration. (E): (a) Hyperplasia toward dermis. (F): (a) Acanthosis. (b) Inflammatory cell infiltration in dermis. (G): (a) Intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies. (b) Vacuolation of granulocytes. (c) Hyperkeratosis. (H): (a) Eosinophilic inclusion bodies. (b) Vacuolation of granulocytes. (I): (a) Eosinophilic inclusion bodies. (b) The proliferation of basal cells in the epidermis. (J): (a) Eosinophilic inclusion bodies. (b) Vacuolation of granulocytes. The tissue stained with hematoxylin and eosin stain and examined under a light microscope and imaged at 10×. All displayed images are represented all detected positive samples.
