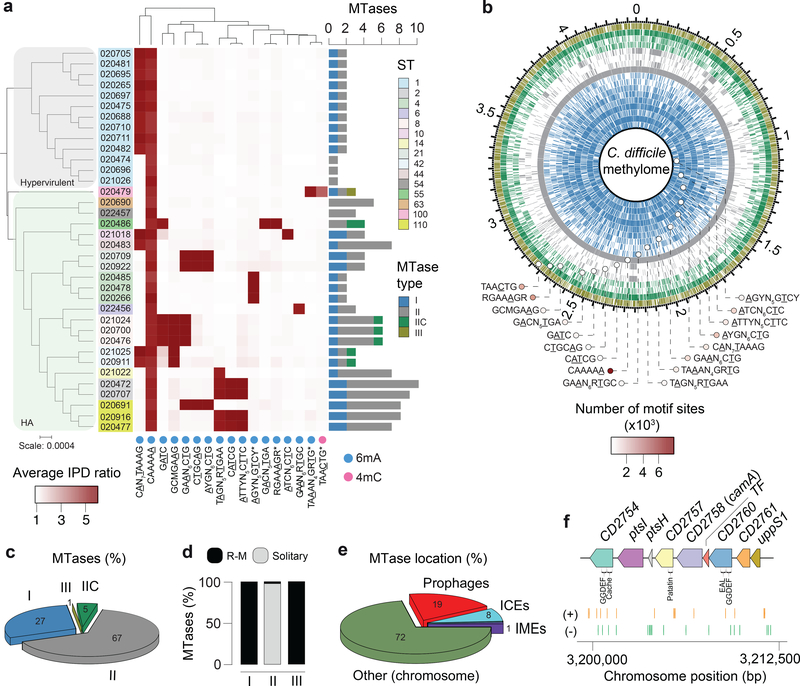
Fig. 1.
Methylomes of the 36 C. difficile strains. (a) Phylogenetic tree of the 36 C. difficile strains colored by clade (hypervirulent, human and animal (HA) associated) and MLST sequence type (ST). Heatmap depicting the landscape of methylated motifs per genome, and their average interpulse duration (IPD) ratio. Asterisks refer to new motifs not previously listed in the reference database REBASE. Methylated bases are underlined. The CAAAAA motif was consistently methylated across isolates. Barplot indicates the number and types of active MTases detected per genome. In Type IIC systems, MTase and REase are encoded in the same polypeptide. (b) Representation of the C. difficile methylome. Shown are the positions of all methylation motif sites in the reference genome of C. difficile 630, colored according to MTase type. Also shown are the average motif occurrences per genome (across the 36 isolates). (c) % of MTases detected according to type. (d) % MTases pertaining to complete R-M systems or without cognate REase (solitary). (e) Breakdown of MTases by location: Integrative Mobile Elements (IMEs), Integrative Conjugative Elements (ICEs), prophages, and other (within the chromosome). No hits were obtained in plasmids. (f) Immediate genomic context of camA. The example shown (including coordinates) refers to the reference genome of C. difficile 630. + / – signs correspond to the sense and antisense strands respectively. Vertical bars correspond to the distribution of the CAAAAA motif. CD2754: phosphodiesterase with a GGDEF domain (PF00990) and a cache domain (PF02743); ptsI and ptsH belong to a phosphotransferase (PTS) system; CD2757: patatin-like phospholipase (PF01734); CD2758 (camA): Type II MTase; CD2759: Rrf2-type transcriptional regulator; CD2760: phosphodiesterase with a GGDEF domain and a conserved EAL domain (PF00563); CD2761: N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase; CD2762: undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase. The genomic context of camA is largely conserved across strains, located ~25 kb upstream of the S-layer biogenesis locus (Extended Data Figs. 4c,d). Several of the genes flanking camA (including itself) are part of the C. difficile core-genome (see below), suggesting that they may play biological roles fundamental to C. difficile.