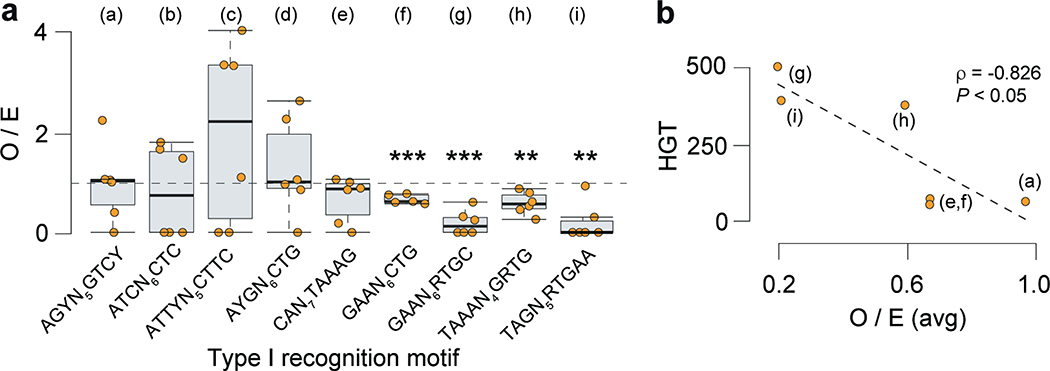
Extended Data Fig. 3. Interplay between Type I R-M systems and gene flux in C. difficile.
Interplay between Type I R-M systems and gene flux in C. difficile. (a) Observed/expected (O/E) ratios for Type I target recognition motifs in Clostridioides phage genomes. 6 phage genomes representative of Siphoviridae and Myoviridae families and tail types were analyzed (ϕCD111, ϕCDHM11, ϕMMP01, ϕMMP04, ϕC2, ϕCD38). O/E values were obtained with R’MES using Markov chain models that take into consideration oligonucleotide composition. For each motif, we tested if the median value of the O/E ratio in phage genomes was significantly different from 1. In box plots, the middle line indicates the median value, boxes are 25th and 75th quartiles, and whiskers indicate 1.5 times the interquartile range. ***P < 10−3; **P < 10 −2 (one-sided one-sample t-test). (b) Relation between HGT and O/E ratio for Type I target recognition motifs. For those C. difficile genomes harboring a single Type I R-M system (i.e., without the confounding effect of multiple systems), we computed the average values of HGT, and plotted these values against the average O/E ratio for the corresponding target recognition motif in phage genomes. This was only possible for the n = 6 motifs indicated in brackets. The spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (ρ) and associated P value (two-sided) is shown.