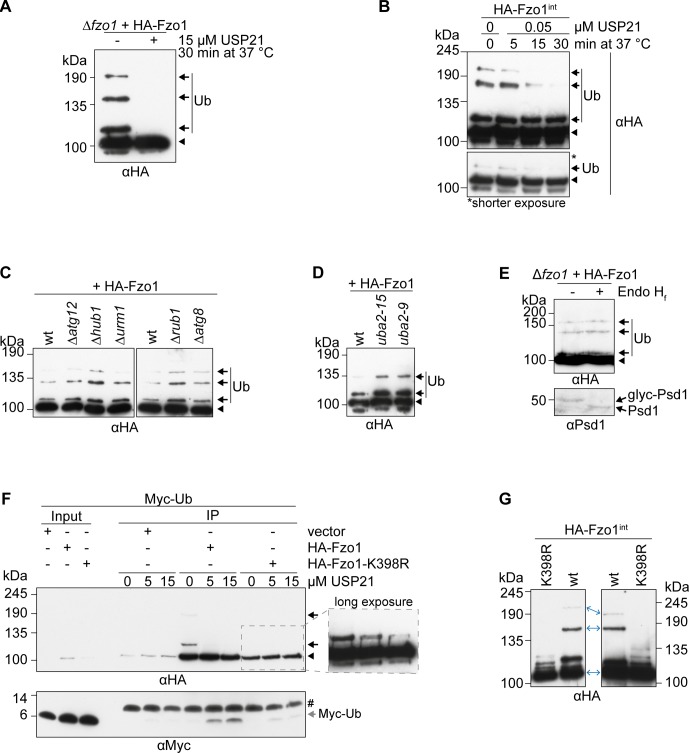
Figure S2. UBLs are not responsible for the conserved ubiquitylation pattern on Fzo1.
(A) Treatment of HA-Fzo1 with USP21. Crude mitochondria prepared from cells expressing HA-Fzo1 were solubilized and incubated with HA-coupled beads. Immunoprecipitated HA-Fzo1 was treated with 15 μM of purified USP21 (or buffer as a negative control) for 30 min at 37°C and then eluted with Laemmli buffer and analysed by SDS–PAGE and Western blot, using an HA-specific antibody. Forms of Fzo1 are indicated as in Fig 1A. (B) Deubiquitylating kinetics of genomically HA-tagged Fzo1. (A) Immunoprecipitated HA-Fzo1 was treated and analysed as in (A), but using 0.05 μM USP21 (of buffer) for 5, 15, or 30 min. Forms of Fzo1 are indicated as in Fig 1A. (C) Analysis of Fzo1 ubiquitylation in UBL modifier mutant strains. Crude mitochondrial extracts from wt or UBL modifier deletion strains ∆atg12, ∆hub1, ∆urm1, ∆rub1, and ∆atg8, expressing HA-Fzo1 were solubilized, subjected to HA-immunoprecipitation and analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using an HA-specific antibody. Forms of Fzo1 are indicated as in Fig 1A. (D) Analysis of Fzo1 ubiquitylation in UBA2 temperature-sensitive mutant strains. Crude mitochondrial extracts from wt or temperature-sensitive UBA2 mutant strains (uba2-15 [H351P] or uba2-9 [L281S]) expressing HA-Fzo1 were solubilized, subjected to HA-immunoprecipitation, and analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using an HA-specific antibody. Forms of Fzo1 are indicated as in Fig 1A. (E) Analysis of Fzo1 glycosylation. Crude mitochondrial extracts were treated with the glycosidase Endo Hf and subsequently analysed by SDS–PAGE and Western blot, using HA- and, as a positive control, Psd1-specific antibodies. Forms of Fzo1 are indicated as in Fig 1A. (F) USP21 treatment of HA-tagged Fzo1 and Fzo1K398R. Strains expressing Myc-tagged ubiquitin (Myc-Ub) as the only form of ubiquitin, additionally expressing HA-tagged Fzo1 or Fzo1K398R (or the empty vector control) were used to isolate crude mitochondrial extracts. Extracts were solubilized and subjected to HA-immunoprecipitation. Proteins bound to HA-coupled beads were treated with the 0, 5, or 15 μM of purified USP21 for 30 min at 37°C. After the treatment, the beads were separated from the supernatant and both parts were analysed by SDS–PAGE and Western blot. The beads fraction was analysed with an HA-specific antibody and the supernatant fraction with a Myc-specific antibody. The inset shows a longer exposure of the selected area. Forms of Fzo1 are indicated as in Fig 1A. #, cross reaction. (G) Comparison of Fzo1 ubiquitylation using different SDS–PAGE conditions. HA-Fzo1 and HA-Fzo1K398R were immunoprecipitated from exponentially growing yeast cells and analysed by SDS–PAGE and Western blot. Left: SDS–PAGE using a 30% acrylamide, 0.8% bis-acrylamide solution, using the HOEFER SDS–PAGE chamber. Right: SDS–Page using a 30% acrylamide, 0.2% bis-acrylamide solution, using the Bio-Rad SDS–PAGE chamber. IP, immunoprecipitation; Myc-Ub, Myc-tagged ubiquitin; Ub, ubiquitin.