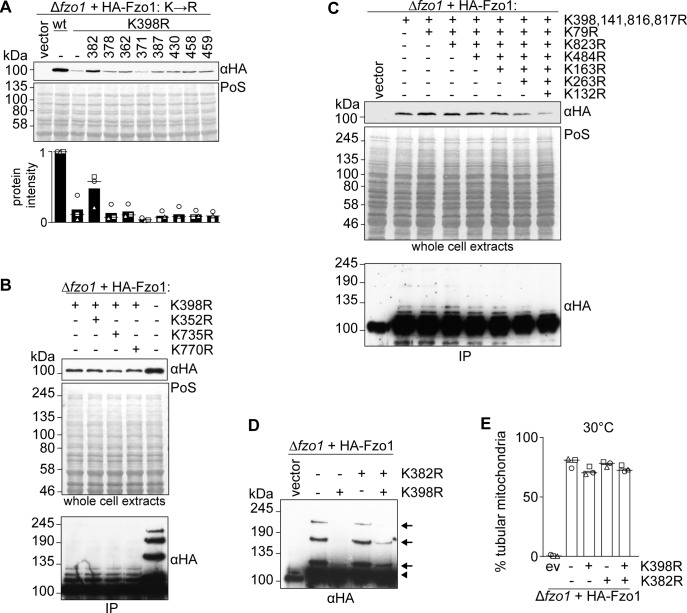
Figure S6. Role of Fzo1 lysines in its protein levels and ubiquitylation.
(A) Steady state levels of HA-tagged Fzo1 variants mutated in surface lysine residues. Total cellular extracts of ∆fzo1 cells expressing the indicated lysine to arginine mutant variants of HA-Fzo1 (as in Fig 4A) or the corresponding empty vector were analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using an HA-specific antibody. The quantification of three independent experiments shows the mean (bar), the median (line), and the individual values (geometric symbols). (B) Role of the conserved lysine residues K352, K735, and K770 in Fzo1 properties. Total cellular extracts (top panel) or HA-Fzo1 immunoprecipitated from solubilized crude mitochondrial extracts (bottom panel), of ∆fzo1 cells expressing the indicated HA-Fzo1 variants, were analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using an HA-specific antibody. (C) Role of lysine residues identified to be ubiquitylated by mass-spectrometry in Fzo1 steady state levels and ubiquitylation profile. Total cellular extracts (Top panel) or crude mitochondrial extracts solubilized and HA-immunoprecipitated HA-Fzo1 (bottom panel) of ∆fzo1 cells expressing the indicated HA-Fzo1 variants were analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using HA-specific antibody. (D) Ubiquitylation of Fzo1 mutated for K398R and/or K382R. Crude mitochondrial extracts from wt or mutants of HA-Fzo1 as indicated were solubilized and subjected to HA-immunoprecipitation. The samples were analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting using an HA-specific antibody. Forms of Fzo1 are indicated as in Fig 1A. (E) Mitochondrial morphology of cells expressing HA-tagged Fzo1-mutated for K398R and/or K382R. Mitochondrial morphology of cells expressing wt or mutants of HA-Fzo1, as indicated, and grown at 30°C was analysed as in Fig 1B. IP, immunoprecipitation; PoS, Ponceau S.